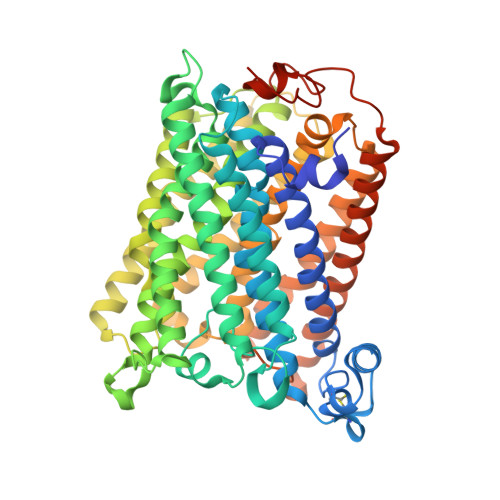
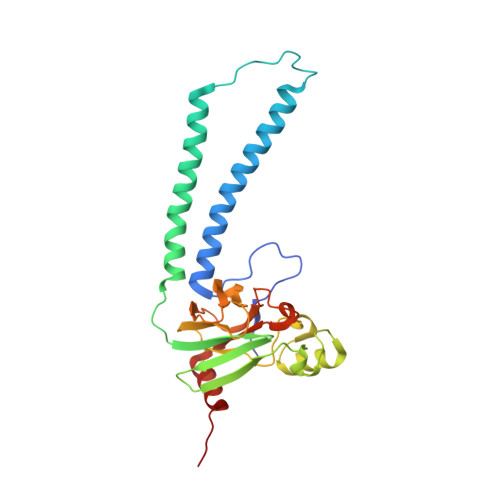
A conserved steroid binding site in cytochrome C oxidase.
Qin, L., Mills, D.A., Buhrow, L., Hiser, C., Ferguson-Miller, S.(2008) Biochemistry 47: 9931-9933
- PubMed: 18759498
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi8013483
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DTU - PubMed Abstract:
Micromolar concentrations of the bile salt deoxycholate are shown to rescue the activity of an inactive mutant, E101A, in the K proton pathway of Rhodobacter sphaeroides cytochrome c oxidase. A crystal structure of the wild-type enzyme reveals, as predicted, deoxycholate bound with its carboxyl group at the entrance of the K path. Since cholate is a known potent inhibitor of bovine oxidase and is seen in a similar position in the bovine structure, the crystallographically defined, conserved steroid binding site could reveal a regulatory site for steroids or structurally related molecules that act on the essential K proton path.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan 48824, USA.