Insights into complement convertase formation based on the structure of the factor B-cobra venom factor complex
Janssen, B.J., Gomes, L., Koning, R.I., Svergun, D.I., Koster, A.J., Fritzinger, D.C., Vogel, C.W., Gros, P.(2009) EMBO J 28: 2469-2478
- PubMed: 19574954
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.184
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3HRZ, 3HS0 - PubMed Abstract:
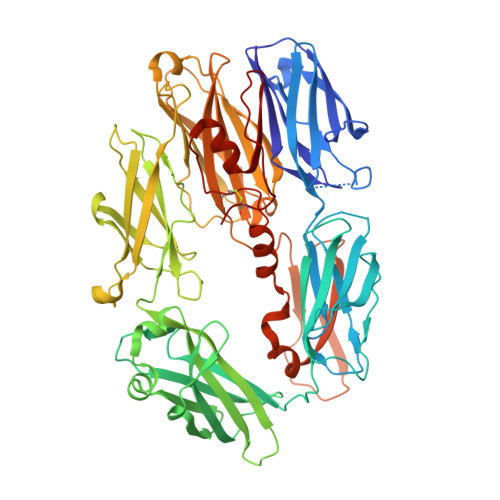
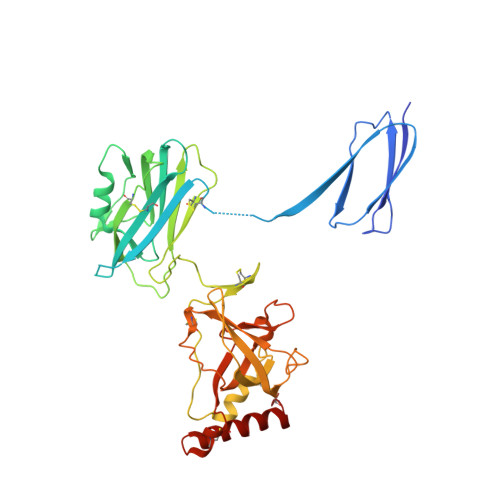
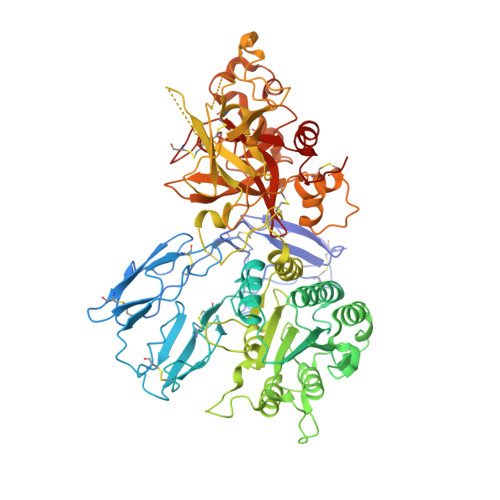
Immune protection by the complement system critically depends on assembly of C3 convertases on the surface of pathogens and altered host cells. These short-lived protease complexes are formed through pro-convertases, which for the alternative pathway consist of the complement component C3b and the pro-enzyme factor B (FB). Here, we present the crystal structure at 2.2-A resolution, small-angle X-ray scattering and electron microscopy (EM) data of the pro-convertase formed by human FB and cobra venom factor (CVF), a potent homologue of C3b that generates more stable convertases. FB is loaded onto CVF through its pro-peptide Ba segment by specific contacts, which explain the specificity for the homologous C3b over the native C3 and inactive products iC3b and C3c. The protease segment Bb binds the carboxy terminus of CVF through the metal-ion dependent adhesion site of the Von Willebrand factor A-type domain. A possible dynamic equilibrium between a 'loading' and 'activation' state of the pro-convertase may explain the observed difference between the crystal structure of CVFB and the EM structure of C3bB. These insights into formation of convertases provide a basis for further development of complement therapeutics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Crystal and Structural Chemistry, Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research, Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands.