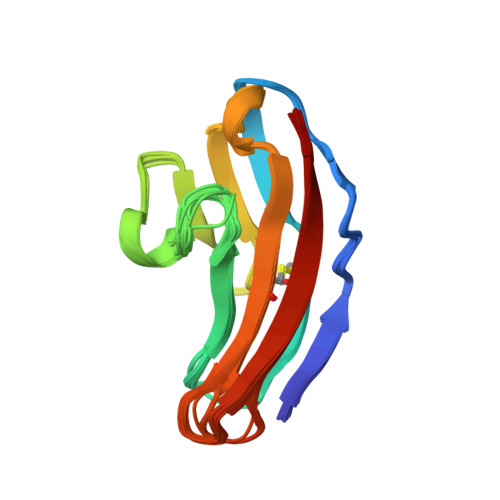
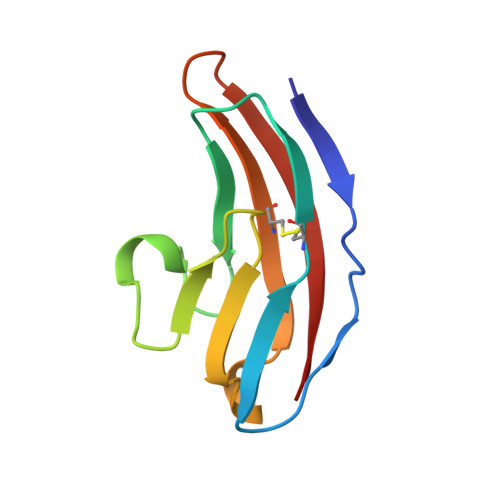
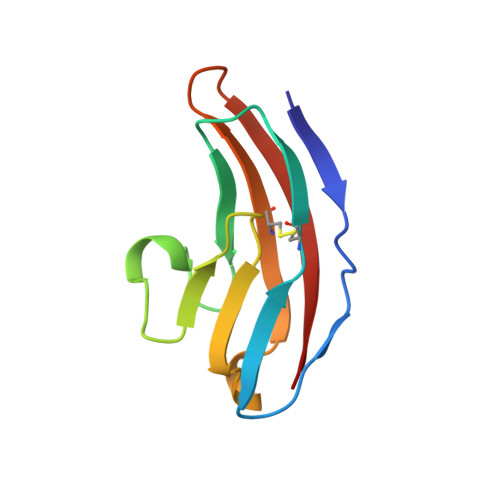
Structure and interactions of NCAM modules 1 and 2, basic elements in neural cell adhesion
Jensen, P.H., Soroka, V., Thomsen, N.K., Ralets, I., Berezin, V., Bock, E., Poulsen, F.M.(1999) Nat Struct Biol 6: 486-493
- PubMed: 10331878
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/8292
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3NCM - PubMed Abstract:
The structure in solution of the second Ig-module fragment of residues 117-208 of NCAM has been determined. Like the first Ig-module of residues 20-116, it belongs to the I set of the immunogloblin superfamily. Module 1 and module 2 interact weakly, and the binding sites of this interaction have been identified. The two-module fragment NCAM(20-208) is a stable dimer. Removal of the charged residues in these sites in NCAM(20-208) abolishes the dimerization. Modeling the dimer of NCAM(20-208) to fit the interactions of these charges produces one coherent binding site for the formation of two antiparallel strands of the first two NCAM modules. This mode of binding could be a major element in trans-cellular interactions in neural cell adhesion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Carlsberg Laboratory, Valby, Denmark.