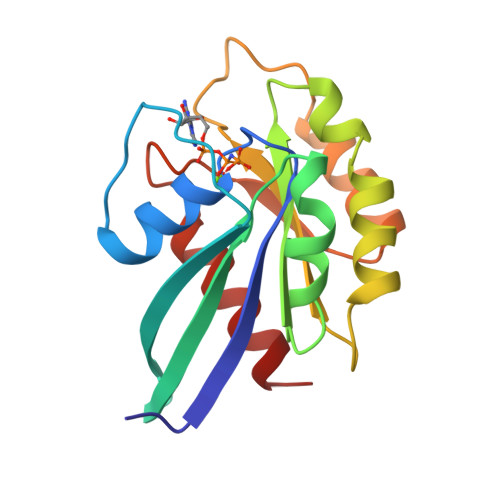
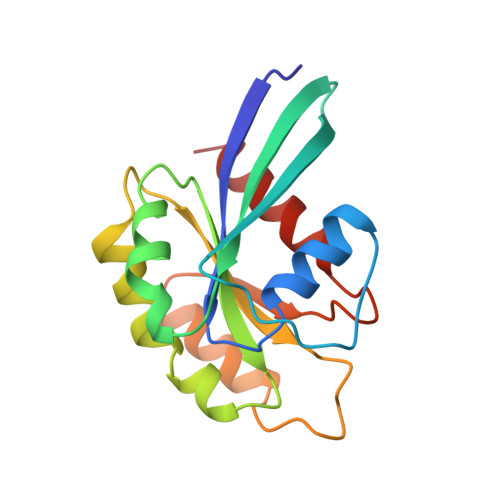
Structural basis of activation and GTP hydrolysis in Rab proteins.
Dumas, J.J., Zhu, Z., Connolly, J.L., Lambright, D.G.(1999) Structure 7: 413-423
- PubMed: 10196122
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80054-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RAB - PubMed Abstract:
Rab proteins comprise a large family of GTPases that regulate vesicle trafficking. Despite conservation of critical residues involved in nucleotide binding and hydrolysis, Rab proteins exhibit low sequence identity with other GTPases, and the structural basis for Rab function remains poorly characterized. The 2. 0 A crystal structure of GppNHp-bound Rab3A reveals the structural determinants that stabilize the active conformation and regulate GTPase activity. The active conformation is stabilized by extensive hydrophobic contacts between the switch I and switch II regions. Serine residues in the phosphate-binding loop (P loop) and switch I region mediate unexpected interactions with the gamma phosphate of GTP that have not been observed in previous GTPase structures. Residues implicated in the interaction with effectors and regulatory factors map to a common face of the protein. The electrostatic potential at the surface of Rab3A indicates a non-uniform distribution of charged and nonpolar residues. The major structural determinants of the active conformation involve residues that are conserved throughout the Rab family, indicating a common mode of activation. Novel interactions with the gamma phosphate impose stereochemical constraints on the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis and provide a structural explanation for the large variation of GTPase activity within the Rab family. An asymmetric distribution of charged and nonpolar residues suggests a plausible orientation with respect to vesicle membranes, positioning predominantly hydrophobic surfaces for interaction with membrane-associated effectors and regulatory factors. Thus, the structure of Rab3A establishes a framework for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the function of Rab GTPases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Molecular Medicine, University of Massachusetts Medical Center, 373 Plantation Street, Worcester, MA 01605, USA.