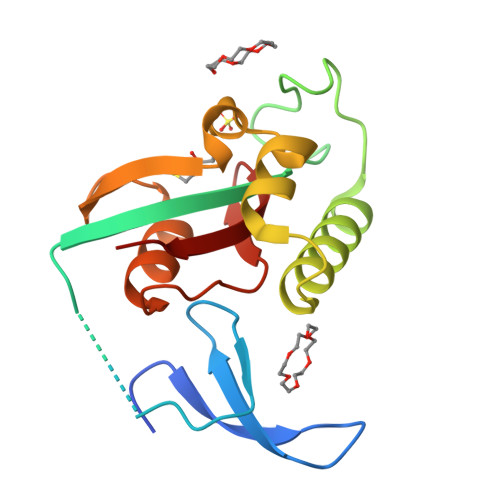
Crowning proteins: modulating the protein surface properties using crown ethers.
Lee, C.C., Maestre-Reyna, M., Hsu, K.C., Wang, H.C., Liu, C.I., Jeng, W.Y., Lin, L.L., Wood, R., Chou, C.C., Yang, J.M., Wang, A.H.(2014) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53: 13054-13058
- PubMed: 25287606
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201405664
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3WH0, 3WHM, 3WUR - PubMed Abstract:
Crown ethers are small, cyclic polyethers that have found wide-spread use in phase-transfer catalysis and, to a certain degree, in protein chemistry. Crown ethers readily bind metallic and organic cations, including positively charged amino acid side chains. We elucidated the crystal structures of several protein-crown ether co-crystals grown in the presence of 18-crown-6. We then employed biophysical methods and molecular dynamics simulations to compare these complexes with the corresponding apoproteins and with similar complexes with ring-shaped low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycols. Our studies show that crown ethers can modify protein surface behavior dramatically by stabilizing either intra- or intermolecular interactions. Consequently, we propose that crown ethers can be used to modulate a wide variety of protein surface behaviors, such as oligomerization, domain-domain interactions, stabilization in organic solvents, and crystallization.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica, 128 Academia Road, Section 2, Nankang, Taipei 11529 (Taiwan); Core Facilities for Protein Structural Analysis, Academia Sinica, 128 Academia Road, Section 2, Nankang, Taipei 11529 (Taiwan).