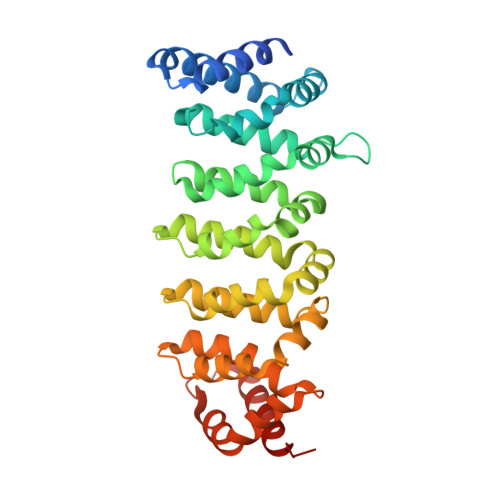
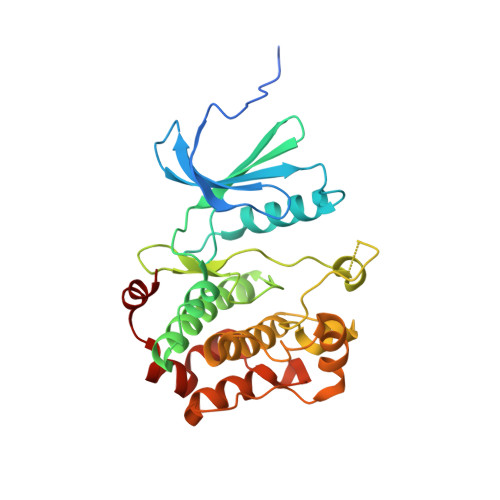
Structural Insights Into the Activation of Mst3 by Mo25.
Mehellou, Y., Alessi, D.R., Macartney, T.J., Szklarz, M., Knapp, S., Elkins, J.M.(2013) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431: 604
- PubMed: 23296203
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.113
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3ZHP - PubMed Abstract:
The MO25 scaffolding protein operates as critical regulator of a number of STE20 family protein kinases (e.g. MST and SPAK isoforms) as well as pseudokinases (e.g. STRAD isoforms that play a critical role in activating the LKB1 tumour suppressor). To better understand how MO25 interacts and stimulates the activity of STE20 protein kinases, we determined the crystal structure of MST3 catalytic domain (residues 19-289) in complex with full length MO25β. The structure reveals an intricate web of interactions between MST3 and MO25β that function to stabilise the kinase domain in a closed, active, conformation even in the absence of ATP or an ATP-mimetic inhibitor. The binding mode of MO25β is reminiscent of the mechanism by which MO25α interacts with the pseudokinase STRADα. In particular we identified interface residues Tyr223 of MO25β and Glu58 and Ile71 of MST3 that when mutated prevent activation of MST3 by MO25β. These data provide molecular understanding of the mechanism by which MO25 isoforms regulates the activity of STE20 family protein kinases.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Protein Phosphorylation Unit, College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee, Dow Street, Dundee, DD1 5EH Scotland, UK. y.mehellou@dundee.ac.uk