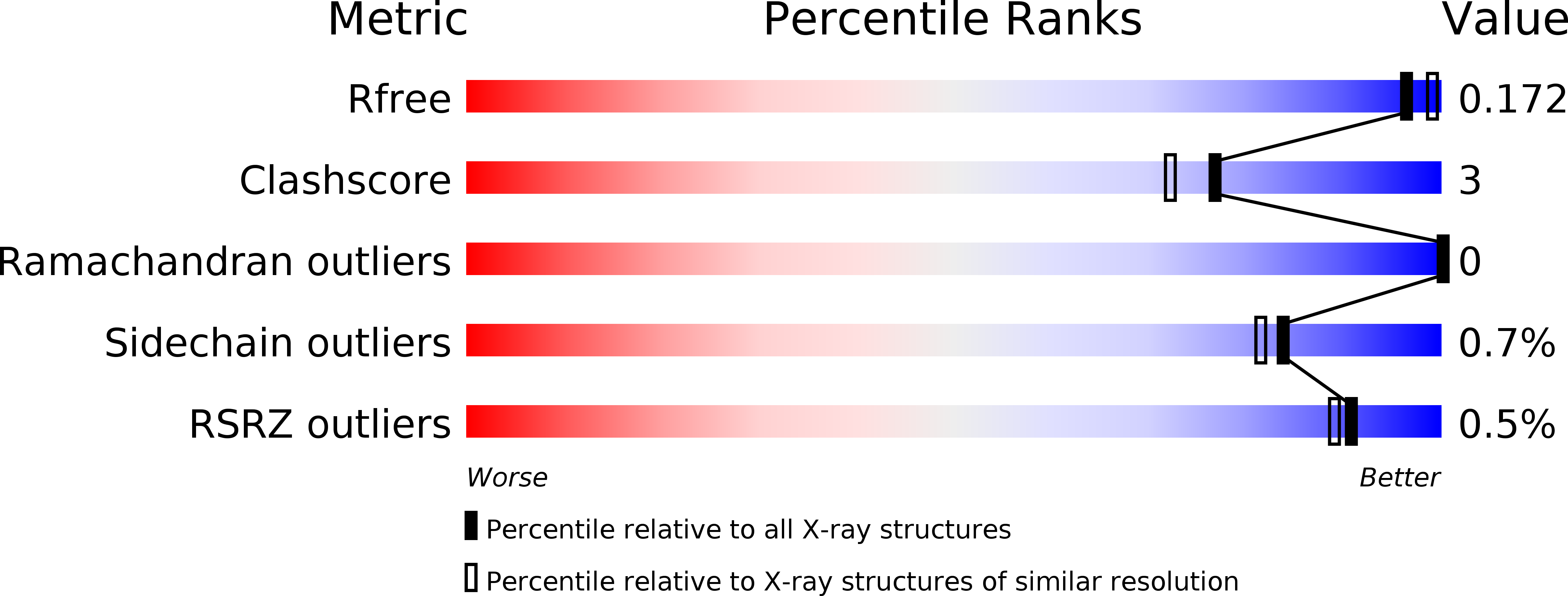
Influenza neuraminidase operates via a nucleophilic mechanism and can be targeted by covalent inhibitors
Vavricka, C.J., Liu, Y., Kiyota, H., Sriwilaijaroen, N., Qi, J., Tanaka, K., Wu, Y., Li, Q., Li, Y., Yan, J., Suzuki, Y., Gao, G.F.(2013) Nat Commun 4: 1491-1491
- PubMed: 23422659
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms2487
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4H52, 4H53 - PubMed Abstract:
Development of novel influenza neuraminidase inhibitors is critical for preparedness against influenza outbreaks. Knowledge of the neuraminidase enzymatic mechanism and transition-state analogue, 2-deoxy-2,3-didehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid, contributed to the development of the first generation anti-neuraminidase drugs, zanamivir and oseltamivir. However, lack of evidence regarding influenza neuraminidase key catalytic residues has limited strategies for novel neuraminidase inhibitor design. Here, we confirm that influenza neuraminidase conserved Tyr406 is the key catalytic residue that may function as a nucleophile; thus, mechanism-based covalent inhibition of influenza neuraminidase was conceived. Crystallographic studies reveal that 2α,3ax-difluoro-N-acetylneuraminic acid forms a covalent bond with influenza neuraminidase Tyr406 and the compound was found to possess potent anti-influenza activity against both influenza A and B viruses. Our results address many unanswered questions about the influenza neuraminidase catalytic mechanism and demonstrate that covalent inhibition of influenza neuraminidase is a promising and novel strategy for the development of next-generation influenza drugs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Research Network of Immunity and Health, Beijing Institutes of Life Science, Beijing 100101, China.