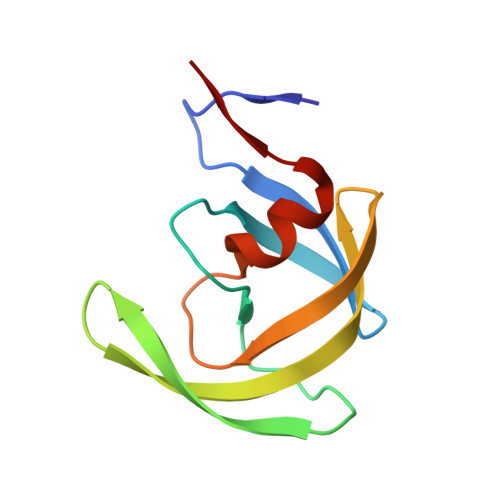
HIV-1 protease-substrate coevolution in nelfinavir resistance.
Kolli, M., Ozen, A., Kurt-Yilmaz, N., Schiffer, C.A.(2014) J Virol 88: 7145-7154
- PubMed: 24719428
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00266-14
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4OBD, 4OBF, 4OBG, 4OBH, 4OBJ, 4OBK - PubMed Abstract:
Resistance to various human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease inhibitors (PIs) challenges the effectiveness of therapies in treating HIV-1-infected individuals and AIDS patients. The virus accumulates mutations within the protease (PR) that render the PIs less potent. Occasionally, Gag sequences also coevolve with mutations at PR cleavage sites contributing to drug resistance. In this study, we investigated the structural basis of coevolution of the p1-p6 cleavage site with the nelfinavir (NFV) resistance D30N/N88D protease mutations by determining crystal structures of wild-type and NFV-resistant HIV-1 protease in complex with p1-p6 substrate peptide variants with L449F and/or S451N. Alterations of residue 30's interaction with the substrate are compensated by the coevolving L449F and S451N cleavage site mutations. This interdependency in the PR-p1-p6 interactions enhances intermolecular contacts and reinforces the overall fit of the substrate within the substrate envelope, likely enabling coevolution to sustain substrate recognition and cleavage in the presence of PR resistance mutations. Resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) protease inhibitors challenges the effectiveness of therapies in treating HIV-1-infected individuals and AIDS patients. Mutations in HIV-1 protease selected under the pressure of protease inhibitors render the inhibitors less potent. Occasionally, Gag sequences also mutate and coevolve with protease, contributing to maintenance of viral fitness and to drug resistance. In this study, we investigated the structural basis of coevolution at the Gag p1-p6 cleavage site with the nelfinavir (NFV) resistance D30N/N88D protease mutations. Our structural analysis reveals the interdependency of protease-substrate interactions and how coevolution may restore substrate recognition and cleavage in the presence of protease drug resistance mutations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA.