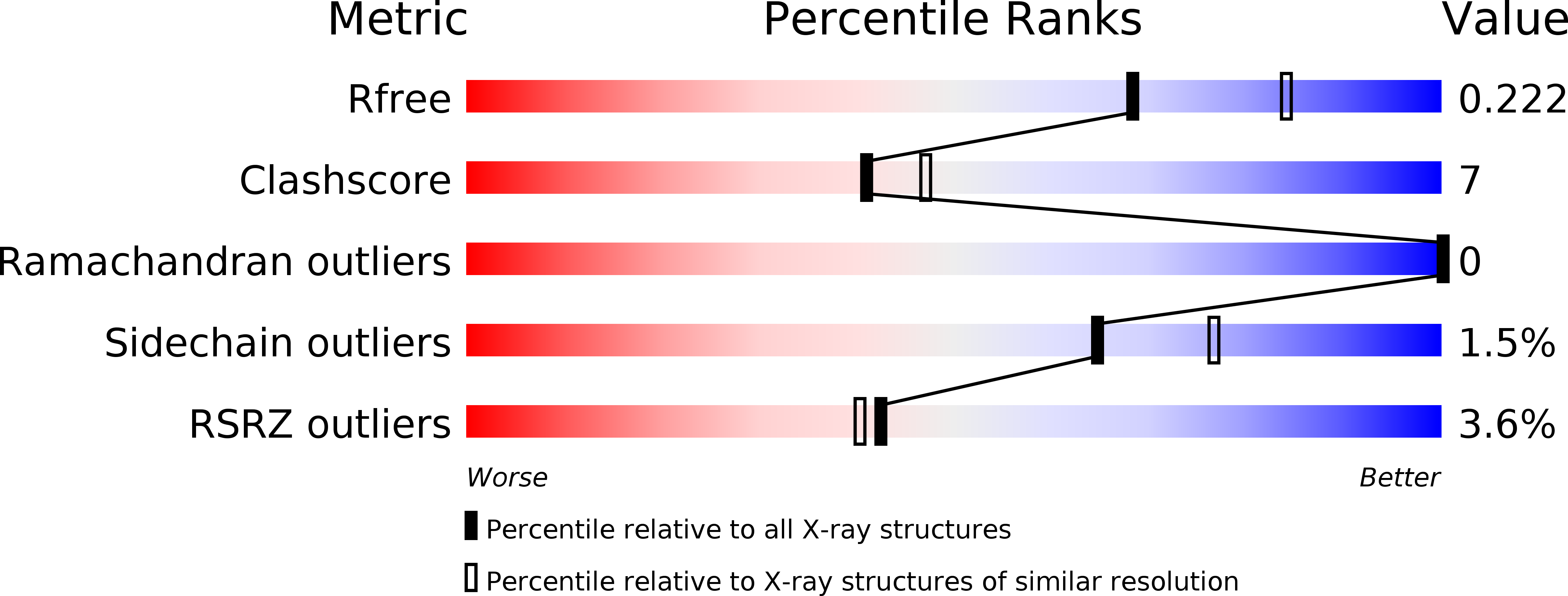
A Catalytic Trisulfide in Human Sulfide Quinone Oxidoreductase Catalyzes Coenzyme A Persulfide Synthesis and Inhibits Butyrate Oxidation.
Landry, A.P., Moon, S., Kim, H., Yadav, P.K., Guha, A., Cho, U.S., Banerjee, R.(2019) Cell Chem Biol 26: 1515-1525.e4
- PubMed: 31591036
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.09.010
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OI5, 6OI6, 6OIB, 6OIC - PubMed Abstract:
Mitochondrial sulfide quinone oxidoreductase (SQR) catalyzes the oxidation of H 2 S to glutathione persulfide with concomitant reduction of CoQ 10 . We report herein that the promiscuous activity of human SQR supported the conversion of CoA to CoA-SSH (CoA-persulfide), a potent inhibitor of butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, and revealed a molecular link between sulfide and butyrate metabolism, which are known to interact. Three different CoQ 1 -bound crystal structures furnished insights into how diverse substrates access human SQR, and provided snapshots of the reaction coordinate. Unexpectedly, the active site cysteines in SQR are configured in a bridging trisulfide at the start and end of the catalytic cycle, and the presence of sulfane sulfur was confirmed biochemically. Importantly, our study leads to a mechanistic proposal for human SQR in which sulfide addition to the trisulfide cofactor eliminates 201 Cys-SSH, forming an intense charge-transfer complex with flavin adenine dinucleotide, and 379 Cys-SSH, which transfers sulfur to an external acceptor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Chemistry, University of Michigan Medical School, Ann Arbor, MI 48109, USA.