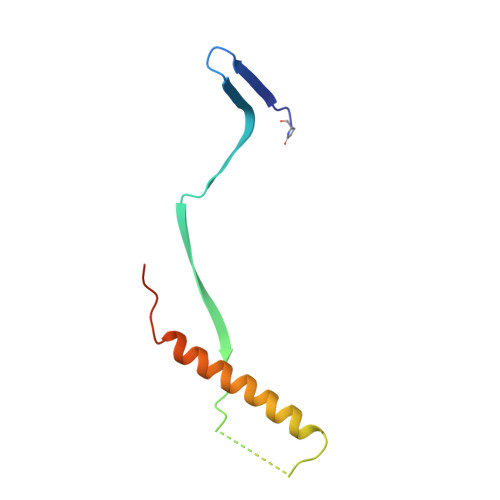
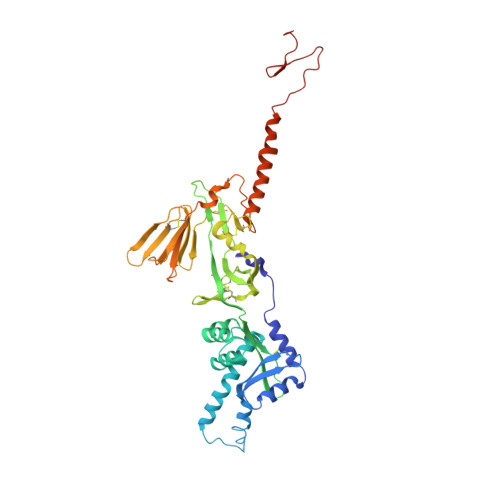
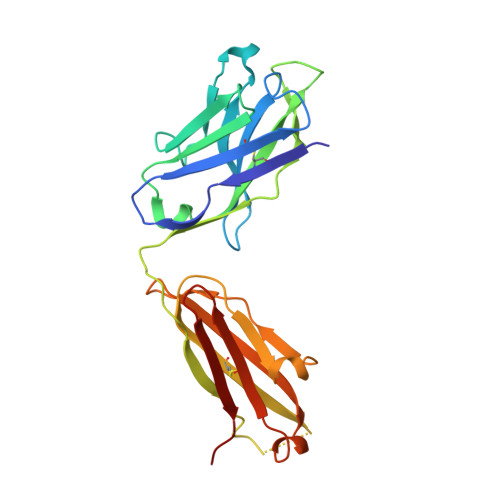
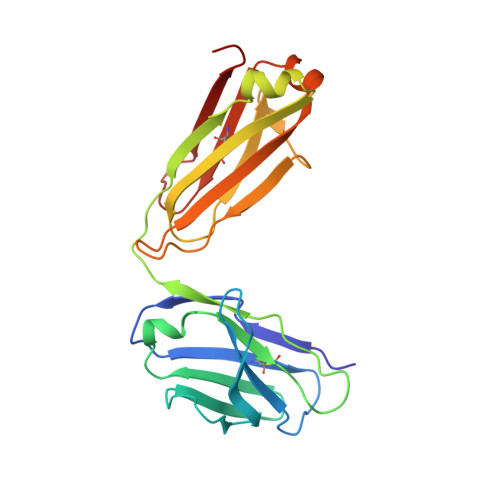
A potent broadly neutralizing human RSV antibody targets conserved site IV of the fusion glycoprotein.
Tang, A., Chen, Z., Cox, K.S., Su, H.P., Callahan, C., Fridman, A., Zhang, L., Patel, S.B., Cejas, P.J., Swoyer, R., Touch, S., Citron, M.P., Govindarajan, D., Luo, B., Eddins, M., Reid, J.C., Soisson, S.M., Galli, J., Wang, D., Wen, Z., Heidecker, G.J., Casimiro, D.R., DiStefano, D.J., Vora, K.A.(2019) Nat Commun 10: 4153-4153
- PubMed: 31515478
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12137-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6OUS - PubMed Abstract:
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection is the leading cause of hospitalization and infant mortality under six months of age worldwide; therefore, the prevention of RSV infection in all infants represents a significant unmet medical need. Here we report the isolation of a potent and broadly neutralizing RSV monoclonal antibody derived from a human memory B-cell. This antibody, RB1, is equipotent on RSV A and B subtypes, potently neutralizes a diverse panel of clinical isolates in vitro and demonstrates in vivo protection. It binds to a highly conserved epitope in antigenic site IV of the RSV fusion glycoprotein. RB1 is the parental antibody to MK-1654 which is currently in clinical development for the prevention of RSV infection in infants.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Infectious Diseases and Vaccines Research, Merck & Co., Inc, West Point, PA, USA.