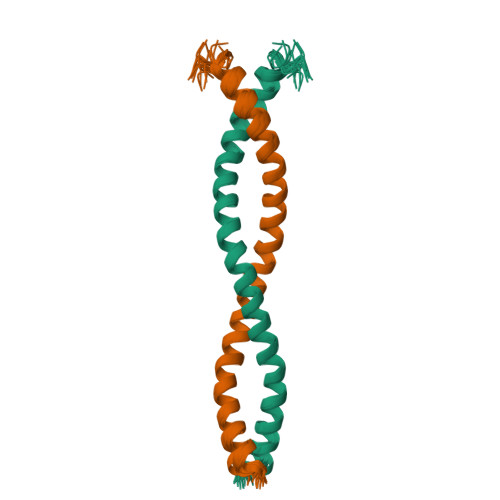
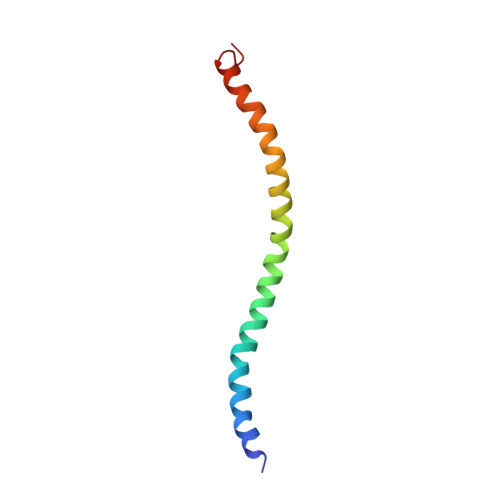
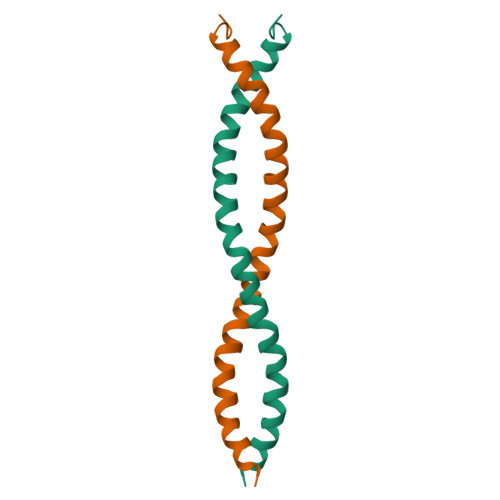
Structural characterization of the self-association domain of swallow.
Loening, N.M., Barbar, E.(2021) Protein Sci 30: 1056-1063
- PubMed: 33641207
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4055
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6XOR - PubMed Abstract:
Swallow, a 62 kDa multidomain protein, is required for the proper localization of several mRNAs involved in the development of Drosophila oocytes. The dimerization of Swallow depends on a 71-residue self-association domain in the center of the protein sequence, and is significantly stabilized by a binding interaction with dynein light chain (LC8). Here, we detail the use of solution-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to characterize the structure of this self-association domain, thereby establishing that this domain forms a parallel coiled-coil and providing insight into how the stability of the dimerization interaction is regulated.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Lewis & Clark College, Portland, Oregon, USA.