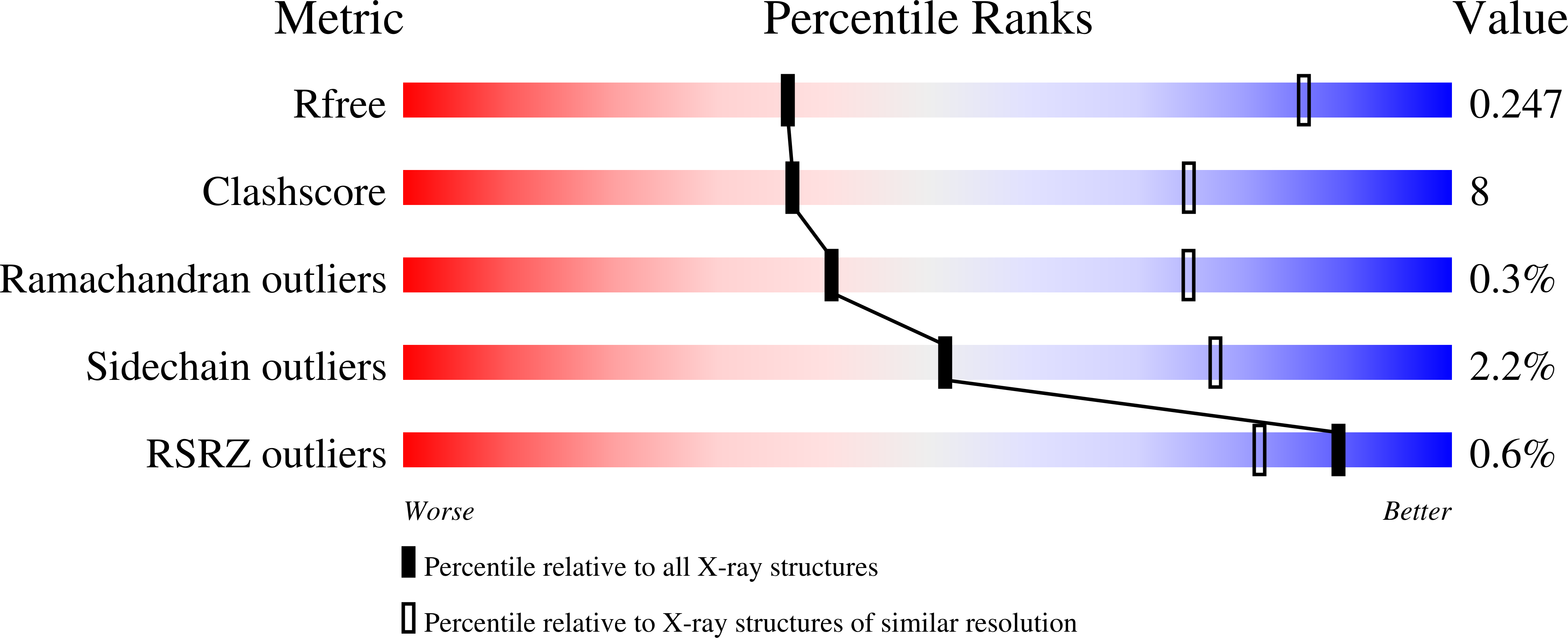
Structure and mechanism of Staphylococcus aureus oleate hydratase (OhyA).
Radka, C.D., Batte, J.L., Frank, M.W., Young, B.M., Rock, C.O.(2021) J Biol Chem 296: 100252-100252
- PubMed: 33376139
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.016818
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KAV, 7KAW, 7KAX, 7KAY, 7KAZ - PubMed Abstract:
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-dependent bacterial oleate hydratases (OhyAs) catalyze the addition of water to isolated fatty acid carbon-carbon double bonds. Staphylococcus aureus uses OhyA to counteract the host innate immune response by inactivating antimicrobial unsaturated fatty acids. Mechanistic information explaining how OhyAs catalyze regiospecific and stereospecific hydration is required to understand their biological functions and the potential for engineering new products. In this study, we deduced the catalytic mechanism of OhyA from multiple structures of S. aureus OhyA in binary and ternary complexes with combinations of ligands along with biochemical analyses of relevant mutants. The substrate-free state shows Arg81 is the gatekeeper that controls fatty acid entrance to the active site. FAD binding engages the catalytic loop to simultaneously rotate Glu82 into its active conformation and Arg81 out of the hydrophobic substrate tunnel, allowing the fatty acid to rotate into the active site. FAD binding also dehydrates the active site, leaving a single water molecule connected to Glu82. This active site water is a hydronium ion based on the analysis of its hydrogen bond network in the OhyA•PEG400•FAD complex. We conclude that OhyA accelerates acid-catalyzed alkene hydration by positioning the fatty acid double bond to attack the active site hydronium ion, followed by the addition of water to the transient carbocation intermediate. Structural transitions within S. aureus OhyA channel oleate to the active site, curl oleate around the substrate water, and stabilize the hydroxylated product to inactivate antimicrobial fatty acids.
Organizational Affiliation:
The Department of Infectious Diseases, St Jude Children's Research Hospital, Memphis, Tennessee, USA.