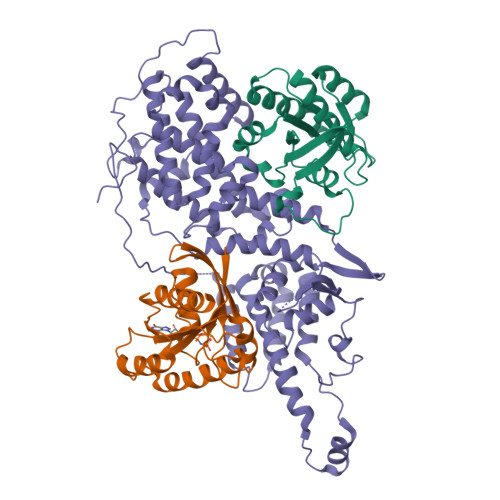
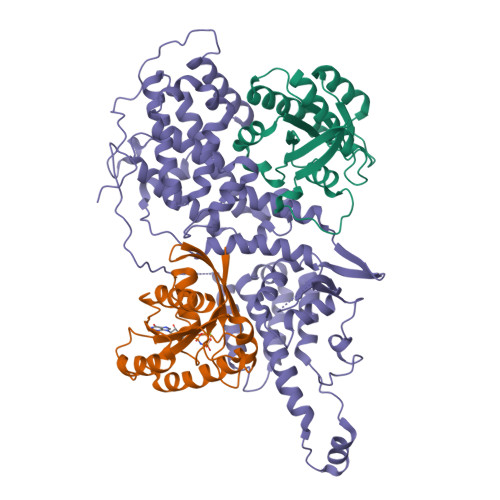
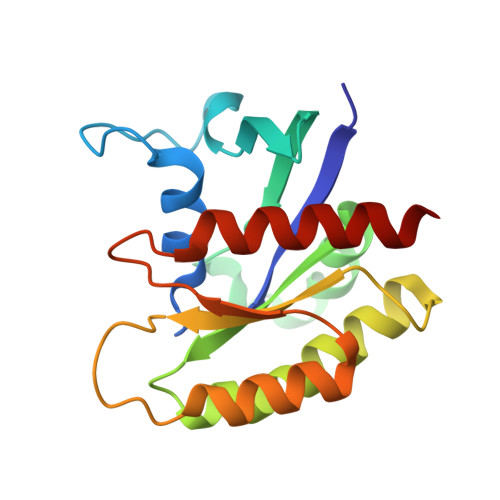
Molecular assemblies of the catalytic domain of SOS with KRas and oncogenic mutants.
Moghadamchargari, Z., Shirzadeh, M., Liu, C., Schrecke, S., Packianathan, C., Russell, D.H., Zhao, M., Laganowsky, A.(2021) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118
- PubMed: 33723061
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2022403118
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7KFZ - PubMed Abstract:
Ras is regulated by a specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor Son of Sevenless (SOS), which facilitates the exchange of inactive, GDP-bound Ras with GTP. The catalytic activity of SOS is also allosterically modulated by an active Ras (Ras-GTP). However, it remains poorly understood how oncogenic Ras mutants interact with SOS and modulate its activity. Here, native ion mobility-mass spectrometry is employed to monitor the assembly of the catalytic domain of SOS (SOS cat ) with KRas and three cancer-associated mutants (G12C, G13D, and Q61H), leading to the discovery of different molecular assemblies and distinct conformers of SOS cat engaging KRas. We also find KRas G13D exhibits high affinity for SOS cat and is a potent allosteric modulator of its activity. A structure of the KRas G13D •SOS cat complex was determined using cryogenic electron microscopy providing insight into the enhanced affinity of the mutant protein. In addition, we find that KRas G13D -GTP can allosterically increase the nucleotide exchange rate of KRas at the active site more than twofold compared to KRas-GTP. Furthermore, small-molecule Ras•SOS disruptors fail to dissociate KRas G13D •SOS cat complexes, underscoring the need for more potent disruptors. Taken together, a better understanding of the interaction between oncogenic Ras mutants and SOS will provide avenues for improved therapeutic interventions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX 77843.