A Phenotypic Screen Identifies Potent DPP9 Inhibitors Capable of Killing HIV-1 Infected Cells.
Moore, K.P., Schwaid, A.G., Tudor, M., Park, S., Beshore, D.C., Converso, A., Shipe, W.D., Anand, R., Lan, P., Moningka, R., Rothman, D.M., Sun, W., Chi, A., Cornella-Taracido, I., Adam, G.C., Bahnck-Teets, C., Carroll, S.S., Fay, J.F., Goh, S.L., Lusen, J., Quan, S., Rodriguez, S., Xu, M., Andrews, C.L., Song, C., Filzen, T., Li, J., Hollenstein, K., Klein, D.J., Lammens, A., Lim, U.M., Fang, Z., McHale, C., Li, Y., Lu, M., Diamond, T.L., Howell, B.J., Zuck, P., Balibar, C.J.(2022) ACS Chem Biol 17: 2595-2604
- PubMed: 36044633
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.2c00515
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
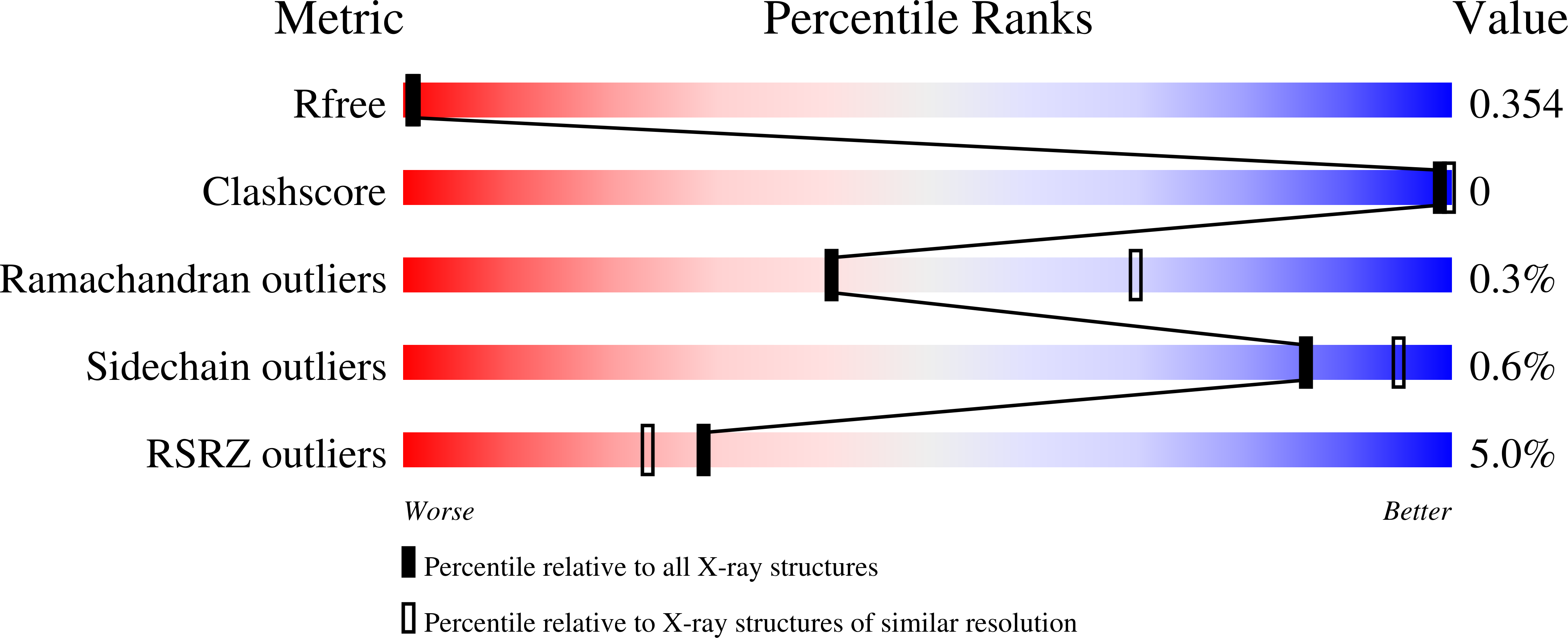
7SVL, 7SVM, 7SVN, 7SVO - PubMed Abstract:
Although current antiretroviral therapy can control HIV-1 replication and prevent disease progression, it is not curative. Identifying mechanisms that can lead to eradication of persistent viral reservoirs in people living with HIV-1 (PLWH) remains an outstanding challenge to achieving cure. Utilizing a phenotypic screen, we identified a novel chemical class capable of killing HIV-1 infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Tool compounds ICeD-1 and ICeD-2 (" i nducer of ce ll d eath-1 and 2"), optimized for potency and selectivity from screening hits, were used to deconvolute the mechanism of action using a combination of chemoproteomic, biochemical, pharmacological, and genetic approaches. We determined that these compounds function by modulating dipeptidyl peptidase 9 (DPP9) and activating the caspase recruitment domain family member 8 (CARD8) inflammasome. Efficacy of ICeD-1 and ICeD-2 was dependent on HIV-1 protease activity and synergistic with efavirenz, which promotes premature activation of HIV-1 protease at high concentrations in infected cells. This in vitro synergy lowers the efficacious cell kill concentration of efavirenz to a clinically relevant dose at concentrations of ICeD-1 or ICeD-2 that do not result in complete DPP9 inhibition. These results suggest engagement of the pyroptotic pathway as a potential approach to eliminate HIV-1 infected cells.
Organizational Affiliation:
Chemical Biology, Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, New Jersey 07065, United States.