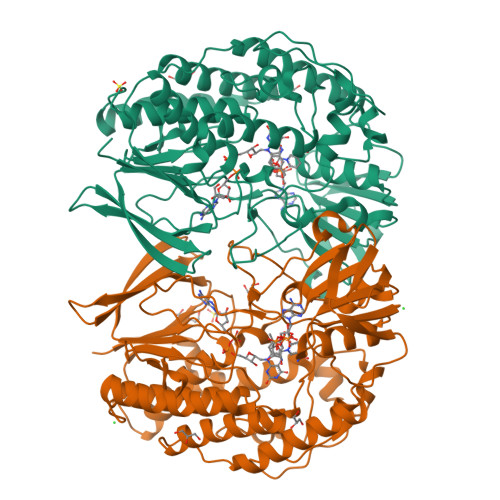
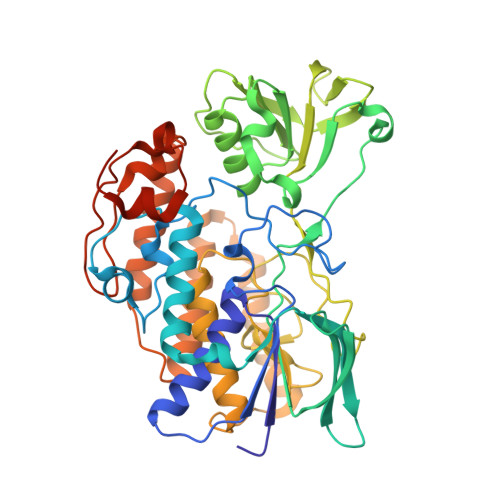
Increased Thermostability of an Engineered Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase to Remediate Trimethylamine in Fish Protein Hydrolysates.
Goris, M., Cea-Rama, I., Puntervoll, P., Ree, R., Almendral, D., Sanz-Aparicio, J., Ferrer, M., Bjerga, G.E.K.(2023) Appl Environ Microbiol 89: e0039023-e0039023
- PubMed: 37222584
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00390-23
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8B2D - PubMed Abstract:
Protein hydrolysates made from marine by-products are very nutritious but frequently contain trimethylamine (TMA), which has an unattractive fish-like smell. Bacterial trimethylamine monooxygenases can oxidize TMA into the odorless trimethylamine N -oxide (TMAO) and have been shown to reduce TMA levels in a salmon protein hydrolysate. To make the flavin-containing monooxygenase (FMO) Methylophaga aminisulfidivorans trimethylamine monooxygenase (mFMO) more suitable for industrial application, we engineered it using the Protein Repair One-Stop Shop (PROSS) algorithm. All seven mutant variants, containing 8 to 28 mutations, displayed increases in melting temperature of between 4.7°C and 9.0°C. The crystal structure of the most thermostable variant, mFMO_20, revealed the presence of four new stabilizing interhelical salt bridges, each involving a mutated residue. Finally, mFMO_20 significantly outperformed native mFMO in its ability to reduce TMA levels in a salmon protein hydrolysate at industrially relevant temperatures. IMPORTANCE Marine by-products are a high-quality source for peptide ingredients, but the unpleasant fishy odor caused by TMA limits their access to the food market. This problem can be mitigated by enzymatic conversion of TMA into the odorless TMAO. However, enzymes isolated from nature must be adapted to industrial requirements, such as the ability to tolerate high temperatures. This study has demonstrated that mFMO can be engineered to become more thermostable. Moreover, unlike the native enzyme, the best thermostable variant efficiently oxidized TMA in a salmon protein hydrolysate at industrial temperatures. Our results present an important next step toward the application of this novel and highly promising enzyme technology in marine biorefineries.
Organizational Affiliation:
NORCE Climate & Environment - NORCE Norwegian Research Centre, Bergen, Norway.