Mapping protein dynamics at high spatial resolution with temperature-jump X-ray crystallography.
Wolff, A.M., Nango, E., Young, I.D., Brewster, A.S., Kubo, M., Nomura, T., Sugahara, M., Owada, S., Barad, B.A., Ito, K., Bhowmick, A., Carbajo, S., Hino, T., Holton, J.M., Im, D., O'Riordan, L.J., Tanaka, T., Tanaka, R., Sierra, R.G., Yumoto, F., Tono, K., Iwata, S., Sauter, N.K., Fraser, J.S., Thompson, M.C.(2023) Nat Chem 15: 1549-1558
- PubMed: 37723259
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01329-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
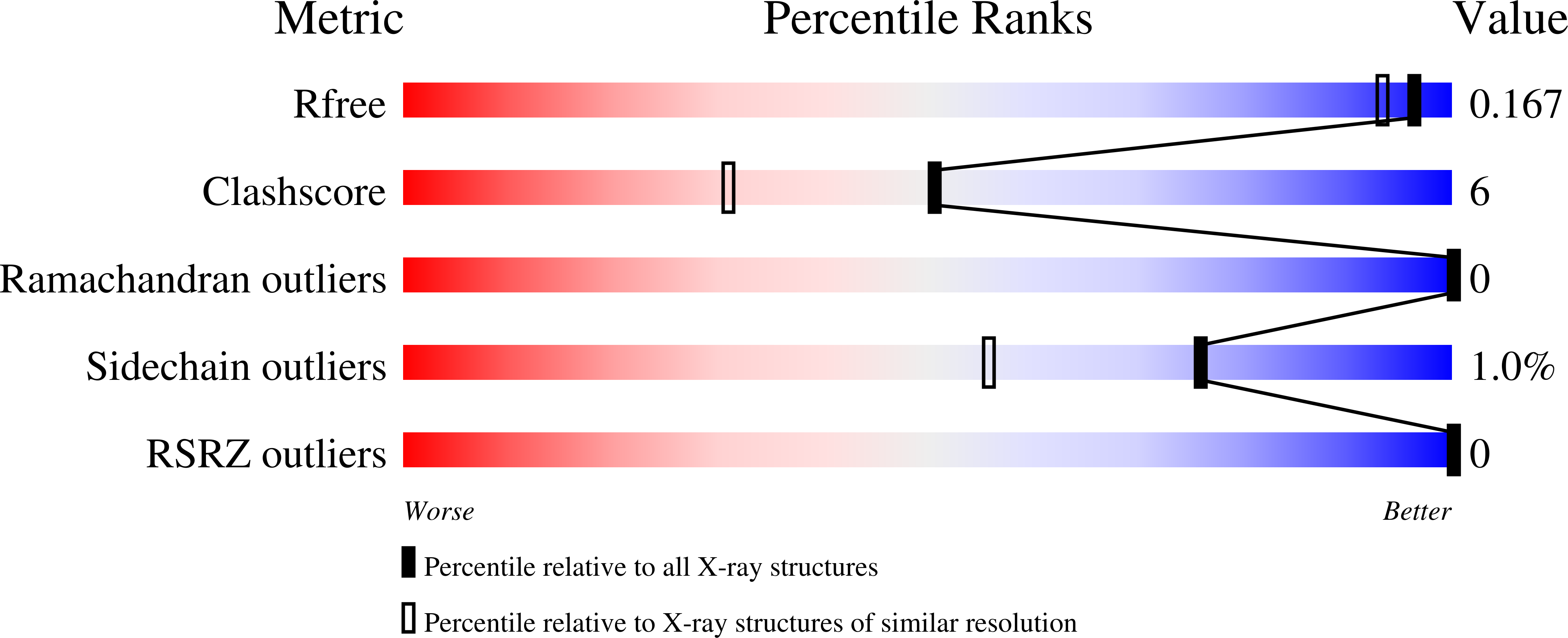
8CVU, 8CVV, 8CVW, 8CW0, 8CW1, 8CW3, 8CW5, 8CW6, 8CW7, 8CW8, 8CWB, 8CWC, 8CWD, 8CWE, 8CWF, 8CWG, 8CWH - PubMed Abstract:
Understanding and controlling protein motion at atomic resolution is a hallmark challenge for structural biologists and protein engineers because conformational dynamics are essential for complex functions such as enzyme catalysis and allosteric regulation. Time-resolved crystallography offers a window into protein motions, yet without a universal perturbation to initiate conformational changes the method has been limited in scope. Here we couple a solvent-based temperature jump with time-resolved crystallography to visualize structural motions in lysozyme, a dynamic enzyme. We observed widespread atomic vibrations on the nanosecond timescale, which evolve on the submillisecond timescale into localized structural fluctuations that are coupled to the active site. An orthogonal perturbation to the enzyme, inhibitor binding, altered these dynamics by blocking key motions that allow energy to dissipate from vibrations into functional movements linked to the catalytic cycle. Because temperature jump is a universal method for perturbing molecular motion, the method demonstrated here is broadly applicable for studying protein dynamics.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of California, Merced, Merced, CA, USA.