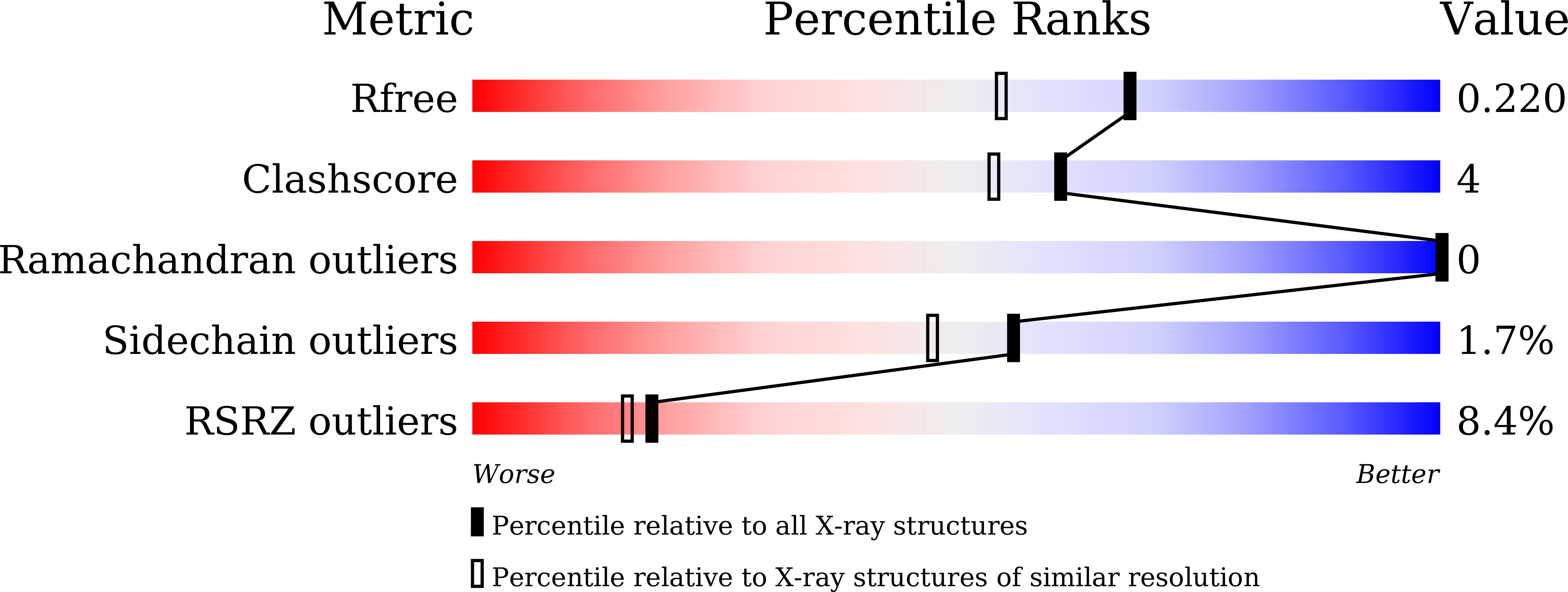
An artificially evolved gene for herbicide-resistant rice breeding.
Dong, J., Yu, X.H., Dong, J., Wang, G.H., Wang, X.L., Wang, D.W., Yan, Y.C., Xiao, H., Ye, B.Q., Lin, H.Y., Yang, G.F.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2407285121-e2407285121
- PubMed: 39133859
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2407285121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8X6Q, 8X74, 8X7C, 8X7D, 8XC3 - PubMed Abstract:
Discovering and engineering herbicide-resistant genes is a crucial challenge in crop breeding. This study focuses on the 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase Inhibitor Sensitive 1-Like (HSL) protein, prevalent in higher plants and exhibiting weak catalytic activity against many β-triketone herbicides (β-THs). The crystal structures of maize HSL1A complexed with β-THs were elucidated, identifying four essential herbicide-binding residues and explaining the weak activity of HSL1A against the herbicides. Utilizing an artificial evolution approach, we developed a series of rice HSL1 mutants targeting the four residues. Then, these mutants were systematically evaluated, identifying the M10 variant as the most effective in modifying β-THs. The initial active conformation of substrate binding in HSL1 was also revealed from these mutants. Furthermore, overexpression of M10 in rice significantly enhanced resistance to β-THs, resulting in a notable 32-fold increase in resistance to methyl-benquitrione. In conclusion, the artificially evolved M10 gene shows great potential for the development of herbicide-resistant crops.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Central China Normal University, Wuhan 430079, People's Republic of China.