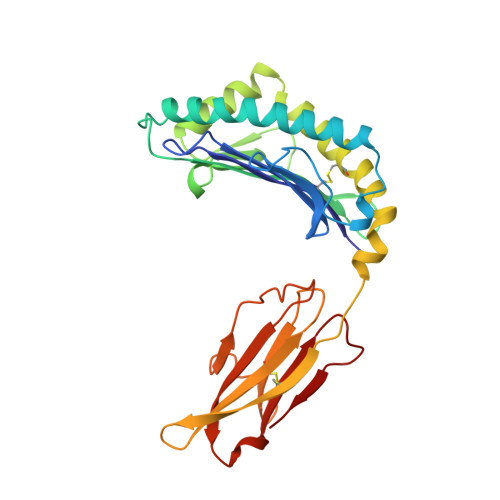
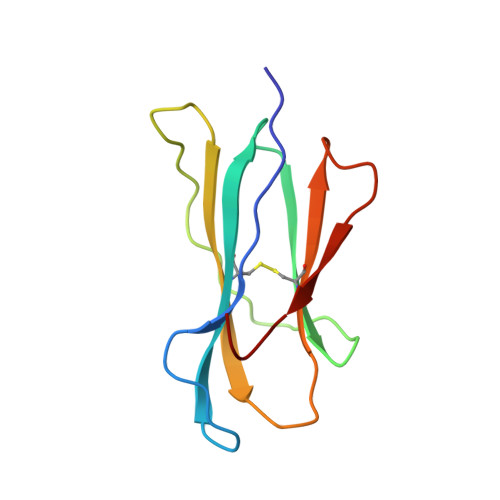
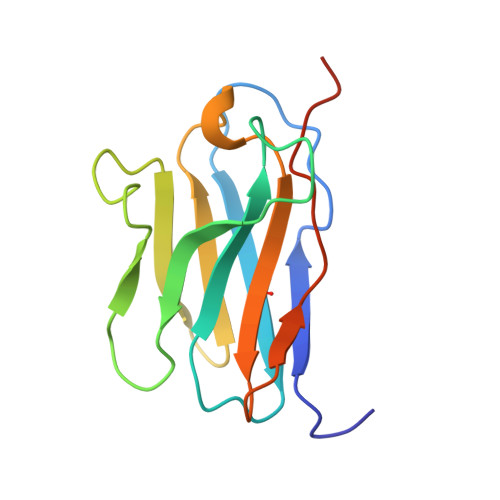
Structural basis of CD8 coreceptor function revealed by crystallographic analysis of a murine CD8alphaalpha ectodomain fragment in complex with H-2Kb.
Kern, P.S., Teng, M.K., Smolyar, A., Liu, J.H., Liu, J., Hussey, R.E., Spoerl, R., Chang, H.C., Reinherz, E.L., Wang, J.H.(1998) Immunity 9: 519-530
- PubMed: 9806638
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80635-4
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BQH - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of the two immunoglobulin variable-like domains of the murine CD8alphaalpha homodimer complexed to the class I MHC H-2Kb molecule at 2.8 A resolution shows that CD8alphaalpha binds to the protruding MHC alpha3 domain loop in an antibody-like manner. Comparison of mouse CD8alphaalpha/H-2Kb and human CD8alphaalpha/HLA-A2 complexes reveals shared as well as species-specific recognition features. In both species, coreceptor function apparently involves the participation of CD8 dimer in a bidentate attachment to an MHC class I molecule in conjunction with a T cell receptor without discernable conformational alteration of the peptide or MHC antigen-presenting platform.
- Laboratory of Immunobiology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts 02115, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: