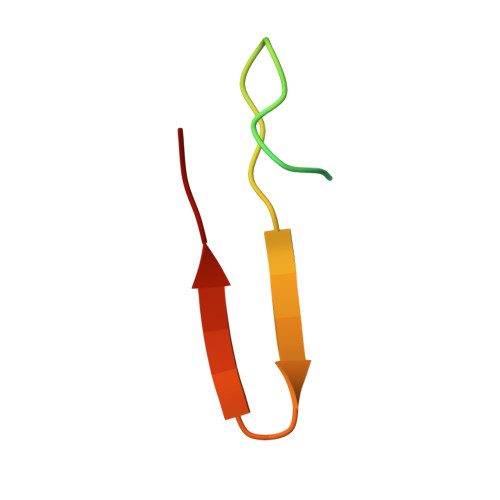
Design and construction of an open multistranded beta-sheet polypeptide stabilized by a disulfide bridge.
Venkatraman, J., Nagana Gowda, G.A., Balaram, P.(2002) J Am Chem Soc 124: 4987-4994
- PubMed: 11982362
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0174276
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1JY4, 1JY6 - PubMed Abstract:
The design and characterization of an open eight-stranded beta-sheet in a synthetic, 2-fold symmetric 70-residue peptide is described. The design strategy involves the generation of a 35-residue four-stranded beta-sheet peptide in which successive hairpins are nucleated by appropriately positioned (D)Pro-Xxx sequences. Oxidative dimerization using a single Cys residue positioned at the center of the C-terminal strand results in a disulfide-bridged eight-stranded structure. Nuclear Overhauser effects firmly establish an eight-stranded beta-sheet in methanol. In water, the outer strands are frayed, but a well-defined four-stranded beta-sheet stabilized by a disulfide bridge and a hydrophobic cluster is determined from NMR data. Comparison of the precursor peptide with the disulfide-bridged dimer reveals considerable enhancement of beta-sheet content in the latter, suggesting that the disulfide cross-link is an effective strategy for the stabilization of beta-sheets.
- Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, India.
Organizational Affiliation: