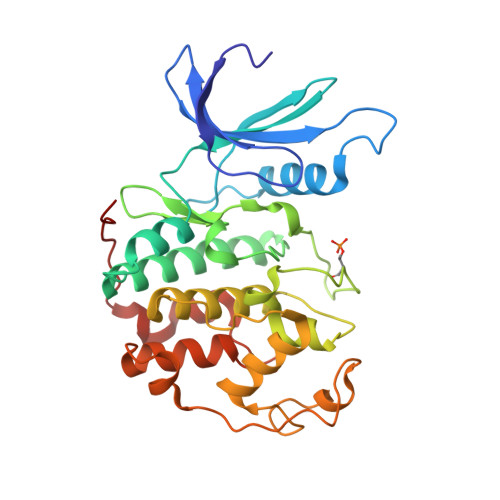
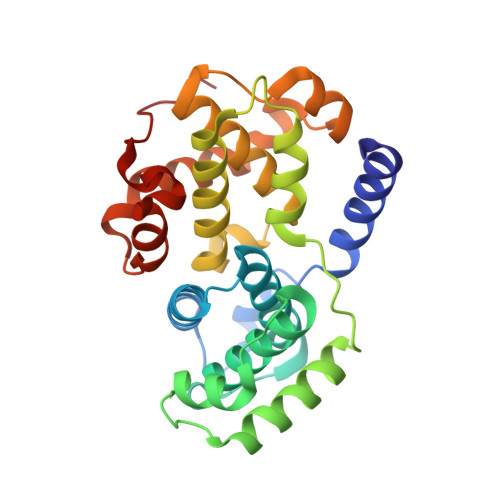
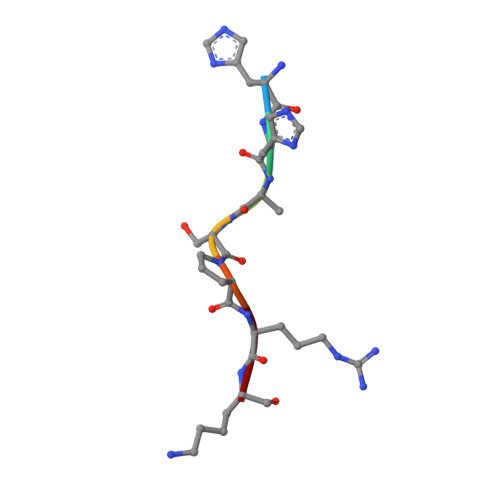
The Structural Basis for Specificity of Substrate and Recruitment Peptides for Cyclin-Dependent Kinases
Brown, N.R., Noble, M.E., Endicott, J.A., Johnson, L.N.(1999) Nat Cell Biol 1: 438
- PubMed: 10559988
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/15674
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QMZ - PubMed Abstract:
Progression through the eukaryotic cell cycle is driven by the orderly activation of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). For activity, CDKs require association with a cyclin and phosphorylation by a separate protein kinase at a conserved threonine residue (T160 in CDK2). Here we present the structure of a complex consisting of phosphorylated CDK2 and cyclin A together with an optimal peptide substrate, HHASPRK. This structure provides an explanation for the specificity of CDK2 towards the proline that follows the phosphorylatable serine of the substrate peptide, and the requirement for the basic residue in the P+3 position of the substrate. We also present the structure of phosphorylated CDK2 plus cyclin A3 in complex with residues 658-668 from the CDK2 substrate p107. These residues include the RXL motif required to target p107 to cyclins. This structure explains the specificity of the RXL motif for cyclins.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics and Oxford Centre for Molecular Sciences, Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Rex Richards Building, South Parks Road, Oxford OX1 3QU, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: