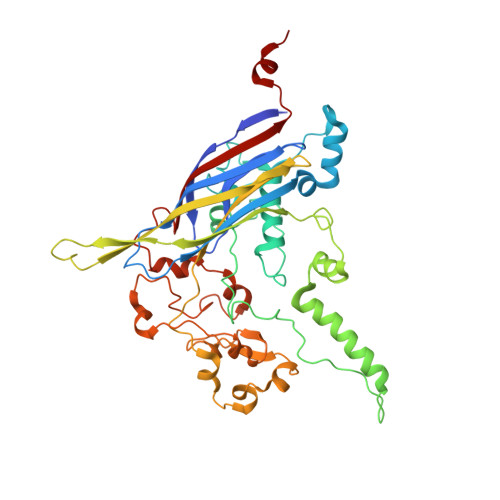
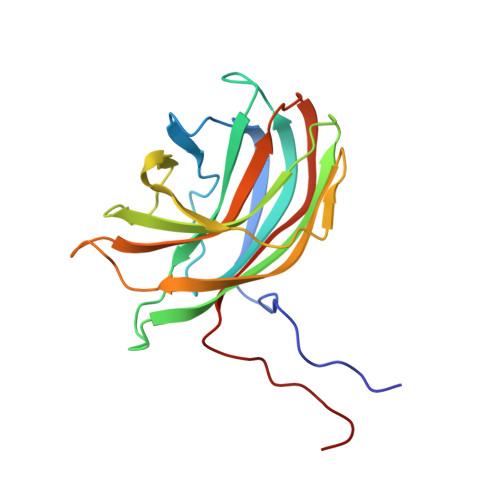
The phiX174 Protein J Mediates DNA Packaging and Viral Attachment to Host Cells.
Bernal, R.A., Hafenstein, S., Esmeralda, R., Fane, B.A., Rossmann, M.G.(2004) J Mol Biology 337: 1109-1122
- PubMed: 15046981
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.02.033
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RB8 - PubMed Abstract:
Packaging of viral genomes into their respective capsids requires partial neutralization of the highly negatively charged RNA or DNA. Many viruses, including the Microviridae bacteriophages phiX174, G4, and alpha3, have solved this problem by coding for a highly positively charged nucleic acid-binding protein that is packaged along with the genome. The phiX174 DNA-binding protein, J, is 13 amino acid residues longer than the alpha3 and G4 J proteins by virtue of an additional nucleic acid-binding domain at the amino terminus. Chimeric phiX174 particles containing the smaller DNA-binding protein cannot be generated due to procapsid instability during DNA packaging. However, chimeric alpha3 and G4 phages, containing the phiX174 DNA-binding protein in place of the endogenous J protein, assemble and are infectious, but are less dense than the respective wild-type species. In addition, host cell attachment and native gel migration assays indicate surface variations of these viruses that are controlled by the nature of the J protein. The structure of alpha3 packaged with phiX174 J protein was determined to 3.5A resolution and compared with the previously determined structures of phiX174 and alpha3. The structures of the capsid and spike proteins in the chimeric particle remain unchanged within experimental error when compared to the wild-type alpha3 virion proteins. The amino-terminal region of the phiX174 J protein, which is missing from wild-type alpha3 virions, is mostly disordered in the alpha3 chimera. The differences observed between solution properties of wild-type phiX174, wild-type alpha3, and alpha3 chimera, including their ability to attach to host cells, correlates with the degree of order in the amino-terminal domain of the J protein. When ordered, this domain binds to the interior of the viral capsid and, thus, might control the flexibility of the capsid. In addition, the properties of the phiX174 J protein in the chimera and the results of mutational analyses suggest that an evolutionary correlation may exist between the size of the J protein and the stoichiometry of the DNA pilot protein H, required in the initial stages of infection. Hence, the function of the J protein is to facilitate DNA packaging, as well as to mediate surface properties such as cell attachment and infection.
- Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University, Lilly Hall, 915 W State Street, West Lafayette, IN 47907-2054, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: