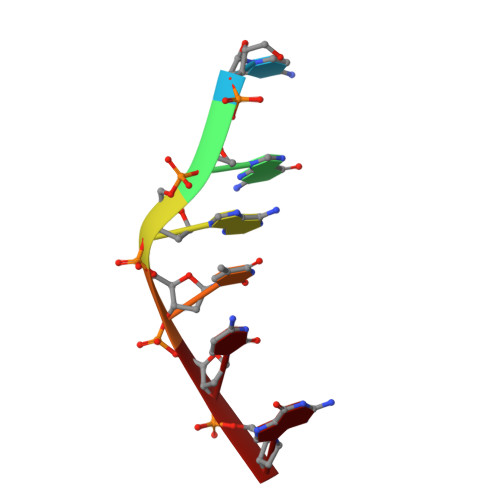
The anticancer agent ellipticine unwinds DNA by intercalative binding in an orientation parallel to base pairs.
Canals, A., Purciolas, M., Aymami, J., Coll, M.(2005) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 61: 1009-1012
- PubMed: 15983425
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444905015404
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Z3F - PubMed Abstract:
Ellipticine is a natural plant product that has been found to be a powerful anticancer drug. Although still unclear, its mechanism of action is considered to be mainly based on DNA intercalation and/or the inhibition of topoisomerase II. Many experimental data suggest an intercalation based on stacking interactions along the major base-pair axis, but alternative binding modes have been proposed, in particular for ellipticine derivatives. The 1.5 A resolution structure of ellipticine complexed to a 6 bp oligonucleotide unveils its mode of binding and enables a detailed analysis of the distorting effects of the drug on the DNA.
- Institut de Biologia Molecular de Barcelona, Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas, Parc Científic de Barcelona, Baldiri Reixac 10-12, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. acpcri@ibmb.csic.es
Organizational Affiliation: