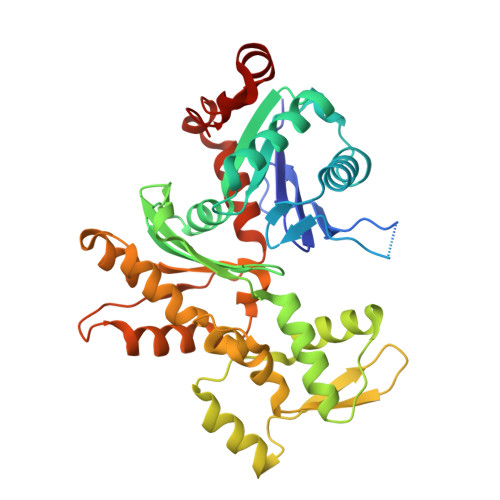
The crystal structure of a cross-linked actin dimer suggests a detailed molecular interface in F-actin
Kudryashov, D.S., Sawaya, M.R., Adisetiyo, H., Norcross, T., Hegyi, G., Reisler, E., Yeates, T.O.(2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 13105-13110
- PubMed: 16141336
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506429102
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2A5X - PubMed Abstract:
The 2.5-A resolution crystal structure is reported for an actin dimer, composed of two protomers cross-linked along the longitudinal (or vertical) direction of the F-actin filament. The crystal structure provides an atomic resolution view of a molecular interface between actin protomers, which we argue represents a near-native interaction in the F-actin filament. The interaction involves subdomains 3 and 4 from distinct protomers. The atomic positions in the interface visualized differ by 5-10 A from those suggested by previous models of F-actin. Such differences fall within the range of uncertainties allowed by the fiber diffraction and electron microscopy methods on which previous models have been based. In the crystal, the translational arrangement of protomers lacks the slow twist found in native filaments. A plausible model of F-actin can be constructed by reintroducing the known filament twist, without disturbing significantly the interface observed in the actin dimer crystal.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Institute, University of California, Los Angeles, CA 90095, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: