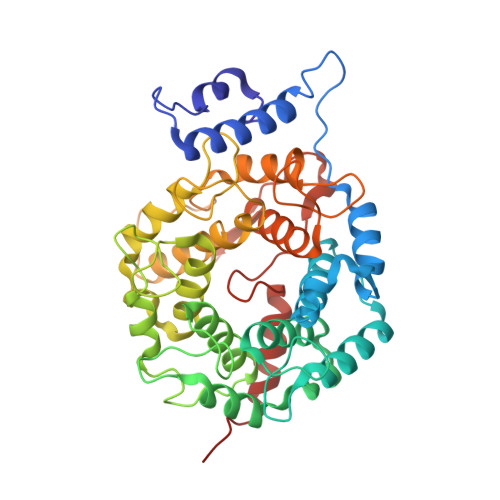
Enhanced FTase activity achieved via piperazine interaction with catalytic zinc.
Njoroge, F.G., Vibulbhan, B., Pinto, P., Strickland, C., Bishop, W.R., Nomeir, A., Girijavallabhan, V.(2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 984-988
- PubMed: 16298128
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2005.10.090
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BED - PubMed Abstract:
Benzocycloheptapyridine tricyclic compounds with piperazine or substituted piperidine moieties extending either from the 5- or 6-position of the tricyclic bridgehead exhibited enhanced FTase activity: this resulted from favorable binding of the ligand nitrogen with the catalytic zinc found in the FTase. A single isomer at C-11 with piperazine adduct extending from the 6-position, compound 24, exhibited excellent FTase activity with IC50 = 0.007 microM, soft agar IC50 = 72 nM, and Rat AUC(PO, 10 mpk) = 4.0 microM x h. X-ray of (-)-[8-chloro-6-(1-piperazinyl)-1H-benzo[5,6]]cyclohepta[1,2-b]pyridine-11-yl]-1-(methylsulfonyl)piperidine 24 bound to Ftase revealed favorable interaction between piperazine nitrogen and catalytic zinc atom.
- Schering-Plough Research Institute, 2015 Galloping Hill Road, K-15-3-3545, Kenilworth, NJ 07033, USA. george.njoroge@spcorp.com
Organizational Affiliation: