Conformational flexibility in the peripheral site of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase revealed by the complex structure with a bifunctional inhibitor.
Colletier, J.P., Sanson, B., Nachon, F., Gabellieri, E., Fattorusso, C., Campiani, G., Weik, M.(2006) J Am Chem Soc 128: 4526-4527
- PubMed: 16594661
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja058683b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
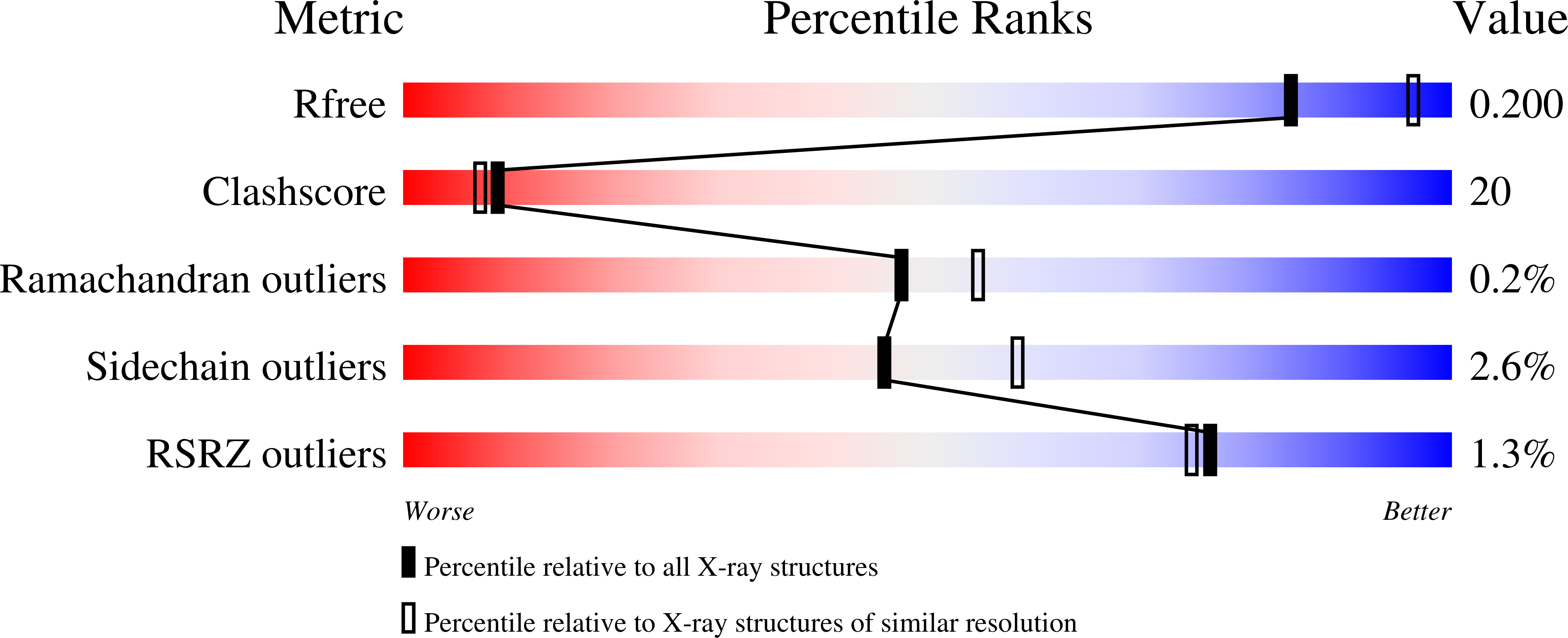
2CEK - PubMed Abstract:
The X-ray crystallographic structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase (TcAChE) in complex with the bifunctional inhibitor NF595, a potentially new anti-Alzheimer drug, has been solved. For the first time in TcAChE, a major conformational change in the peripheral-site tryptophan residue is observed upon complexation. The observed conformational flexibility highlights the dynamic nature of protein structures and is of importance for structure-based drug design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratoire de Biophysique Moléculaire, Institut de Biologie Structurale, 38027 Grenoble, France.