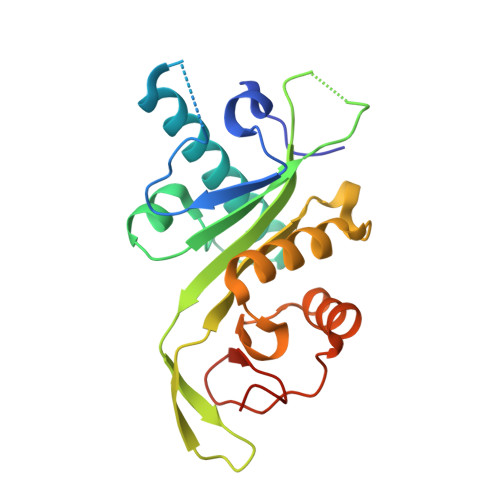
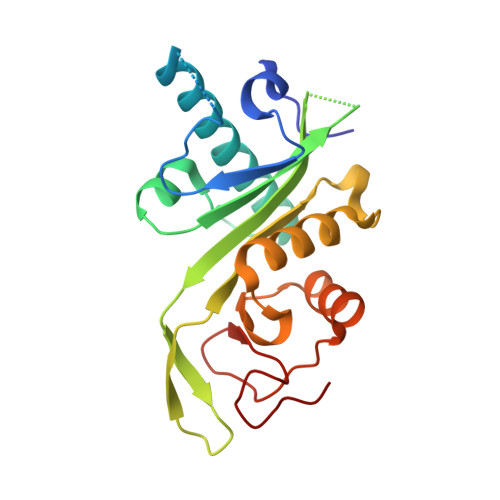
Atomic Resolution Structure of Human Alpha-Tubulin Acetyltransferase Bound to Acetyl-Coa.
Taschner, M., Vetter, M., Lorentzen, E.(2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109: 19649
- PubMed: 23071318
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209343109
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4B5O, 4B5P - PubMed Abstract:
Acetylation of lysine residues is an important posttranslational modification found in all domains of life. α-Tubulin is specifically acetylated on lysine 40, a modification that serves to stabilize microtubules of axons and cilia. Whereas histone acetyltransferases have been extensively studied, there is no structural and mechanistic information available on α-tubulin acetyltransferases. Here, we present the structure of the human α-tubulin acetyltransferase catalytic domain bound to its cosubstrate acetyl-CoA at 1.05 Å resolution. Compared with other lysine acetyltransferases of known structure, α-tubulin acetyltransferase displays a relatively well-conserved cosubstrate binding pocket but is unique in its active site and putative α-tubulin binding site. Using acetylation assays with structure-guided mutants, we map residues important for acetyl-CoA binding, substrate binding, and catalysis. This analysis reveals a basic patch implicated in substrate binding and a conserved glutamine residue required for catalysis, demonstrating that the family of α-tubulin acetyltransferases uses a reaction mechanism different from other lysine acetyltransferases characterized to date.
- Department of Structural Cell Biology, Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, D-82152 Martinsried, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: