The refinement and the structure of the dimer of alpha-chymotrypsin at 1.67-A resolution.
Blevins, R.A., Tulinsky, A.(1985) J Biological Chem 260: 4264-4275
- PubMed: 3980476
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb5cha/pdb
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5CHA - PubMed Abstract:
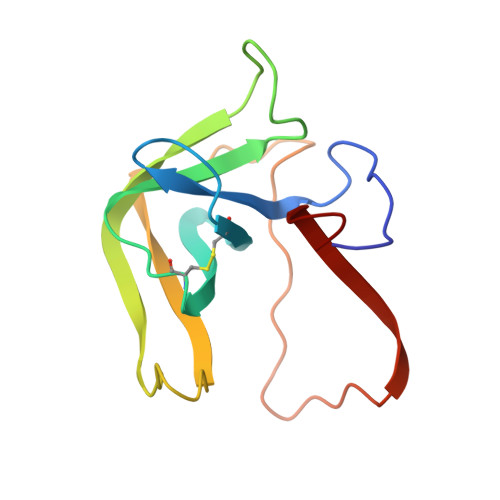
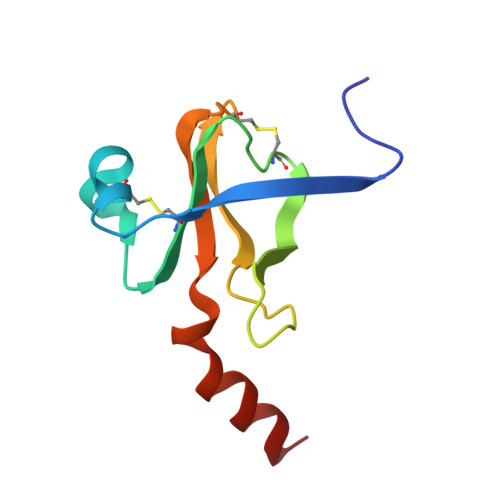
The two molecules of the asymmetric unit of the pH 3.5 conformer of alpha-chymotrypsin have been refined at 1.67-A resolution using restrained least squares methods with Hendrickson's program (PROLSQ). The final R factor is 0.179 (including 247 water molecules). The folding of the main chain of the independent molecules is the same within experimental error but the same does not generally apply to the side chain stereochemistry. From this we conclude that the folding of a protein structure is basically independent of most of the detailed stereochemistry of its side chains. The side chains of the interface region between the independent molecules display pronounced asymmetry. This asymmetry suggests that dynamic and asymmetrical structural changes take place at the time of oligomerization leading to more energetically favorable interactions for the dimer. Comparison of the structures of the independent molecules of alpha-chymotrypsin with the structure of monomeric gamma-chymotrypsin revealed that although the folding of the three molecules is essentially the same, numerous and significant differences pervade the side chain stereochemistry attributable to general flexibility. The specificity site of alpha-chymotrypsin is occupied by ordered water molecules in a similar way to gamma-chymotrypsin and other proteins. Some of these water molecules are displaced when substrate binds to the enzyme, while the others appear to help identify and position the aromatic side chain in catalysis.