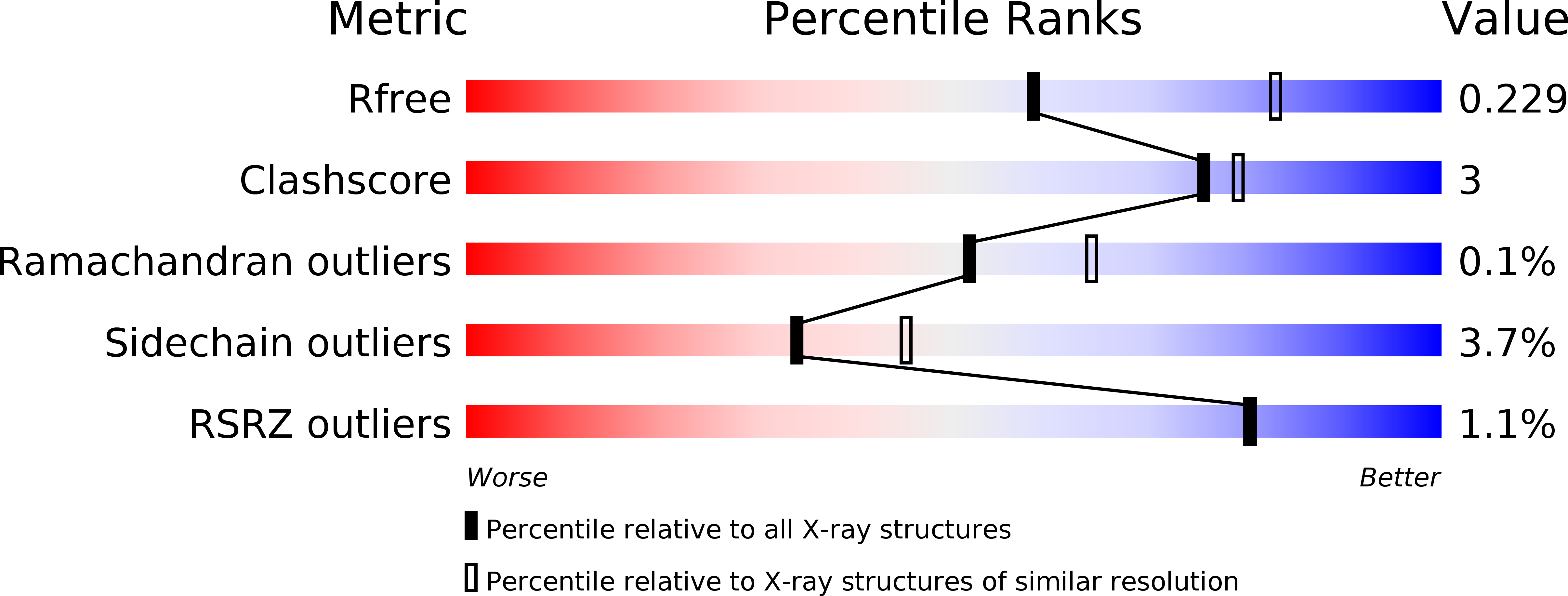
Nanomolar Inhibitors of Glycogen Phosphorylase Based on beta-d-Glucosaminyl Heterocycles: A Combined Synthetic, Enzyme Kinetic, and Protein Crystallography Study.
Bokor, E., Kyriakis, E., Solovou, T.G.A., Koppany, C., Kantsadi, A.L., Szabo, K.E., Szakacs, A., Stravodimos, G.A., Docsa, T., Skamnaki, V.T., Zographos, S.E., Gergely, P., Leonidas, D.D., Somsak, L.(2017) J Med Chem 60: 9251-9262
- PubMed: 28925695
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01056
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5O50, 5O52, 5O54, 5O56 - PubMed Abstract:
Aryl substituted 1-(β-d-glucosaminyl)-1,2,3-triazoles as well as C-β-d-glucosaminyl 1,2,4-triazoles and imidazoles were synthesized and tested as inhibitors against muscle and liver isoforms of glycogen phosphorylase (GP). While the N-β-d-glucosaminyl 1,2,3-triazoles showed weak or no inhibition, the C-β-d-glucosaminyl derivatives had potent activity, and the best inhibitor was the 2-(β-d-glucosaminyl)-4(5)-(2-naphthyl)-imidazole with a K i value of 143 nM against human liver GPa. An X-ray crystallography study of the rabbit muscle GPb inhibitor complexes revealed structural features of the strong binding and offered an explanation for the differences in inhibitory potency between glucosyl and glucosaminyl derivatives and also for the differences between imidazole and 1,2,4-triazole analogues.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Organic Chemistry, University of Debrecen , POB 400, H-4002 Debrecen, Hungary.