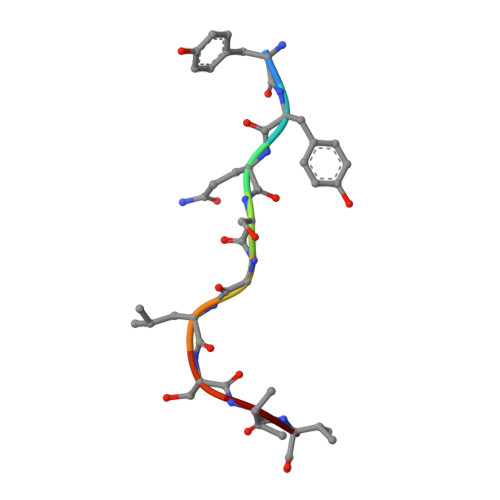
MHC-restricted Ag85B-specific CD8+T cells are enhanced by recombinant BCG prime and DNA boost immunization in mice.
Komine-Aizawa, S., Jiang, J., Mizuno, S., Hayakawa, S., Matsuo, K., Boyd, L.F., Margulies, D.H., Honda, M.(2019) Eur J Immunol
- PubMed: 31135967
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201847988
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TRZ, 5TS1 - PubMed Abstract:
Despite efforts to develop effective treatments and vaccines, Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), particularly pulmonary Mtb, continues to provide major health challenges worldwide. To improve immunization against the persistent health challenge of Mtb infection, we have studied the CD8 + T cell response to Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and recombinant BCG (rBCG) in mice. Here, we generated CD8 + T cells with an rBCG-based vaccine encoding the Ag85B protein of M. kansasii, termed rBCG-Mkan85B, followed by boosting with plasmid DNA expressing the Ag85B gene (DNA-Mkan85B). We identified two MHC-I (H2-K d )-restricted epitopes that induce cross-reactive responses to Mtb and other related mycobacteria in both BALB/c (H2 d ) and CB6F1 (H2 b/d ) mice. The H2-K d -restricted peptide epitopes elicited polyfunctional CD8 + T cell responses that were also highly cross-reactive with those of other proteins of the Ag85 complex. Tetramer staining indicated that the two H2-K d -restricted epitopes elicit distinct CD8 + T cell populations, a result explained by the X-ray structure of the two peptide/H2-K d complexes. These results suggest that rBCG-Mkan85B vector-based immunization and DNA-Mkan85B boost may enhance CD8 + T cell response to Mtb, and might help to overcome the limited effectiveness of the current BCG in eliciting tuberculosis immunity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Microbiology, Department of Pathology and Microbiology, Nihon University School of Medicine, Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan.