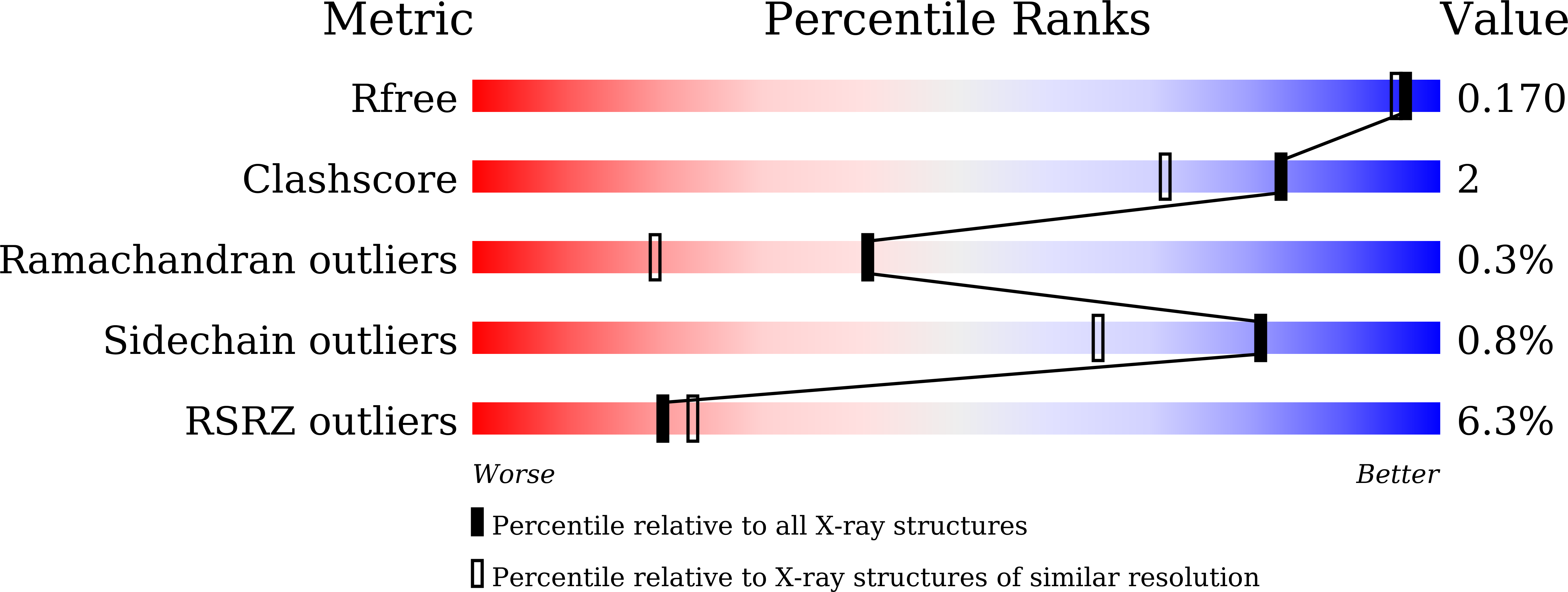
The flavin mononucleotide cofactor in alpha-hydroxyacid oxidases exerts its electrophilic/nucleophilic duality in control of the substrate-oxidation level.
Lyu, S.Y., Lin, K.H., Yeh, H.W., Li, Y.S., Huang, C.M., Wang, Y.L., Shih, H.W., Hsu, N.S., Wu, C.J., Li, T.L.(2019) Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 75: 918-929
- PubMed: 31588923
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S2059798319011938
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ZZP, 5ZZR, 5ZZZ, 6A08, 6A0V, 6A13, 6A19, 6A1H, 6A1L, 6A1M, 6A1P, 6A1R, 6A21, 6A23, 6A3T - PubMed Abstract:
The Y128F single mutant of p-hydroxymandelate oxidase (Hmo) is capable of oxidizing mandelate to benzoate via a four-electron oxidative decarboxylation reaction. When benzoylformate (the product of the first two-electron oxidation) and hydrogen peroxide (an oxidant) were used as substrates the reaction did not proceed, suggesting that free hydrogen peroxide is not the committed oxidant in the second two-electron oxidation. How the flavin mononucleotide (FMN)-dependent four-electron oxidation reaction takes place remains elusive. Structural and biochemical explorations have shed new light on this issue. 15 high-resolution crystal structures of Hmo and its mutants liganded with or without a substrate reveal that oxidized FMN (FMN ox ) possesses a previously unknown electrophilic/nucleophilic duality. In the Y128F mutant the active-site perturbation ensemble facilitates the polarization of FMN ox to a nucleophilic ylide, which is in a position to act on an α-ketoacid, forming an N5-acyl-FMN red dead-end adduct. In four-electron oxidation, an intramolecular disproportionation reaction via an N5-alkanol-FMN red C'α carbanion intermediate may account for the ThDP/PLP/NADPH-independent oxidative decarboxylation reaction. A synthetic 5-deaza-FMN ox cofactor in combination with an α-hydroxyamide or α-ketoamide biochemically and structurally supports the proposed mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Genomics Research Center, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan.