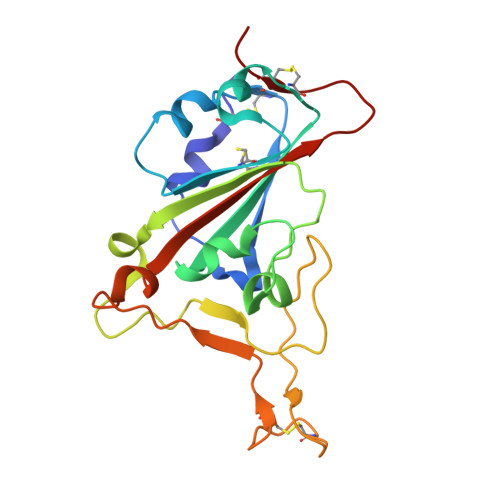
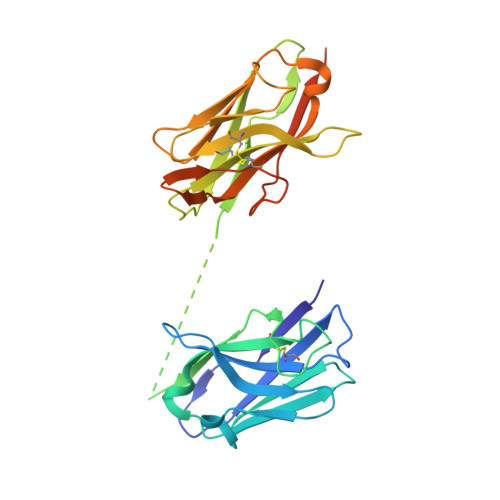
Structure-guided multivalent nanobodies block SARS-CoV-2 infection and suppress mutational escape
Koenig, P.A., Das, H., Liu, H., Kummerer, B.M., Gohr, F.N., Jenster, L.M., Schiffelers, L.D.J., Tesfamariam, Y.M., Uchima, M., Wuerth, J.D., Gatterdam, K., Ruetalo, N., Christensen, M.H., Fandrey, C.I., Normann, S., Todtmann, J.M.P., Pritzl, S., Hanke, L., Boos, J., Yuan, M., Zhu, X., Schmid-Burgk, J.L., Kato, H., Schindler, M., Wilson, I.A., Geyer, M., Ludwig, K.U., Hallberg, B.M., Wu, N.C., Schmidt, F.I.(2021) Science 371
- PubMed: 33436526
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abe6230
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7B14, 7B17, 7B18, 7KN5, 7KN6, 7KN7, 7KSG - PubMed Abstract:
The pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) continues to spread, with devastating consequences. For passive immunization efforts, nanobodies have size and cost advantages over conventional antibodies. In this study, we generated four neutralizing nanobodies that target the receptor binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. We used x-ray crystallography and cryo-electron microscopy to define two distinct binding epitopes. On the basis of these structures, we engineered multivalent nanobodies with more than 100 times the neutralizing activity of monovalent nanobodies. Biparatopic nanobody fusions suppressed the emergence of escape mutants. Several nanobody constructs neutralized through receptor binding competition, whereas other monovalent and biparatopic nanobodies triggered aberrant activation of the spike fusion machinery. These premature conformational changes in the spike protein forestalled productive fusion and rendered the virions noninfectious.
Organizational Affiliation:
Core Facility Nanobodies, Medical Faculty, University of Bonn, 53127 Bonn, Germany. pakoenig@uni-bonn.de martin.hallberg@ki.se nicwu@illinois.edu fschmidt@uni-bonn.de.