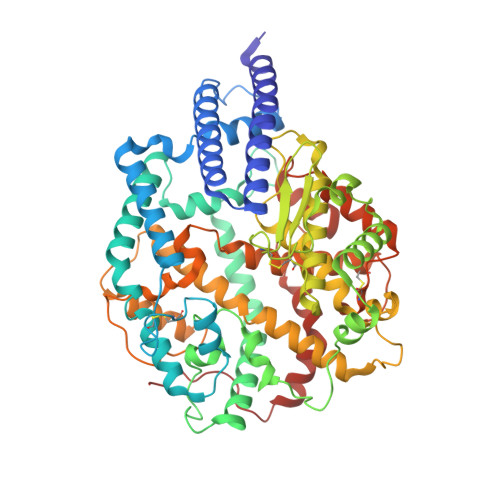
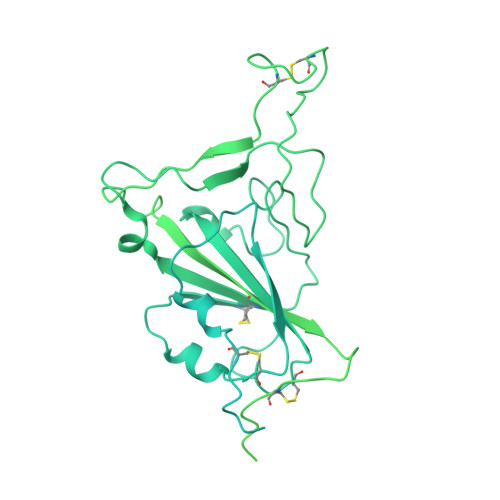
Structural and functional characterizations of infectivity and immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron.
Cui, Z., Liu, P., Wang, N., Wang, L., Fan, K., Zhu, Q., Wang, K., Chen, R., Feng, R., Jia, Z., Yang, M., Xu, G., Zhu, B., Fu, W., Chu, T., Feng, L., Wang, Y., Pei, X., Yang, P., Xie, X.S., Cao, L., Cao, Y., Wang, X.(2022) Cell 185: 860-871.e13
- PubMed: 35120603
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WG6, 7WG7, 7WG8, 7WG9, 7WGB, 7WGC - PubMed Abstract:
The SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant with increased fitness is spreading rapidly worldwide. Analysis of cryo-EM structures of the spike (S) from Omicron reveals amino acid substitutions forging interactions that stably maintain an active conformation for receptor recognition. The relatively more compact domain organization confers improved stability and enhances attachment but compromises the efficiency of the viral fusion step. Alterations in local conformation, charge, and hydrophobic microenvironments underpin the modulation of the epitopes such that they are not recognized by most NTD- and RBD-antibodies, facilitating viral immune escape. Structure of the Omicron S bound with human ACE2, together with the analysis of sequence conservation in ACE2 binding region of 25 sarbecovirus members, as well as heatmaps of the immunogenic sites and their corresponding mutational frequencies, sheds light on conserved and structurally restrained regions that can be used for the development of broad-spectrum vaccines and therapeutics.
- CAS Key Laboratory of Infection and Immunity, National Laboratory of Macromolecules, Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
Organizational Affiliation: