Computational remodeling of an enzyme conformational landscape for altered substrate selectivity.
St-Jacques, A.D., Rodriguez, J.M., Eason, M.G., Foster, S.M., Khan, S.T., Damry, A.M., Goto, N.K., Thompson, M.C., Chica, R.A.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 6058-6058
- PubMed: 37770431
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41762-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
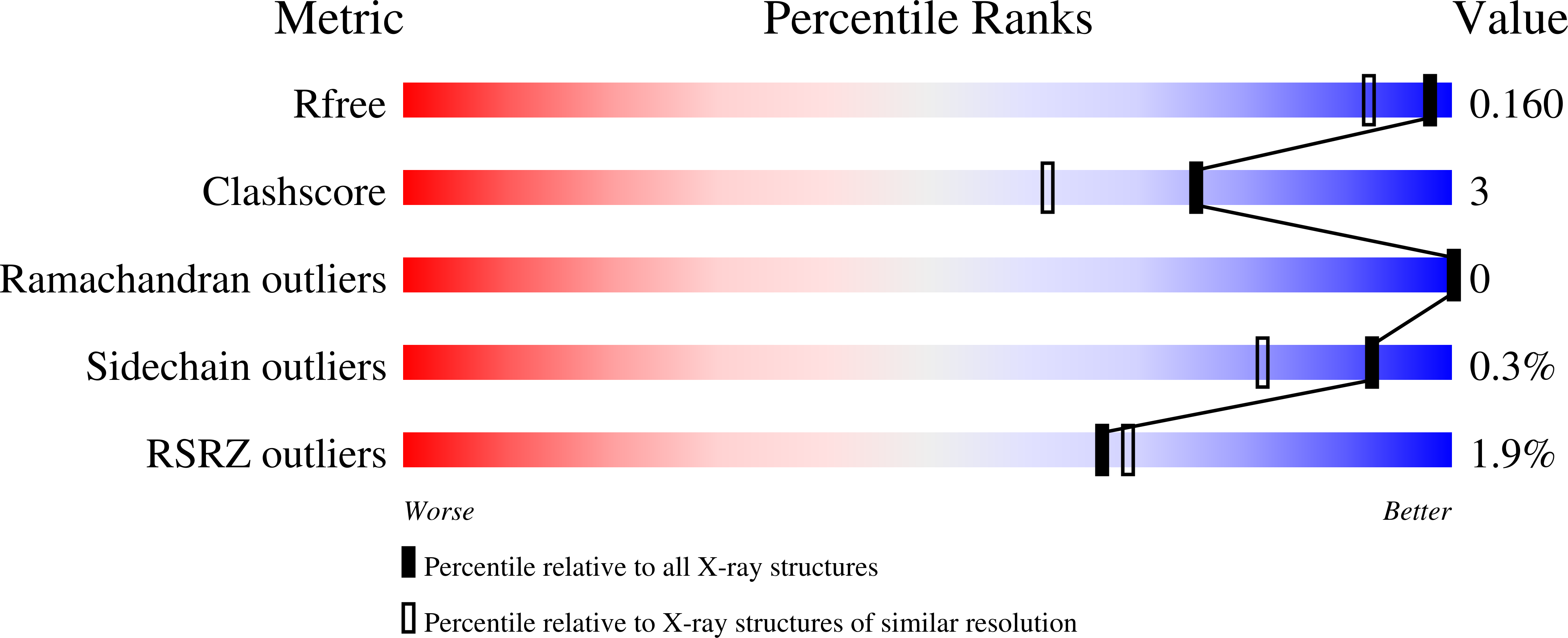
8E9C, 8E9D, 8E9J, 8E9K, 8E9L, 8E9M, 8E9N, 8E9O, 8E9P, 8E9Q, 8E9R, 8E9S, 8E9T, 8E9U, 8E9V - PubMed Abstract:
Structural plasticity of enzymes dictates their function. Yet, our ability to rationally remodel enzyme conformational landscapes to tailor catalytic properties remains limited. Here, we report a computational procedure for tuning conformational landscapes that is based on multistate design of hinge-mediated domain motions. Using this method, we redesign the conformational landscape of a natural aminotransferase to preferentially stabilize a less populated but reactive conformation and thereby increase catalytic efficiency with a non-native substrate, resulting in altered substrate selectivity. Steady-state kinetics of designed variants reveals activity increases with the non-native substrate of approximately 100-fold and selectivity switches of up to 1900-fold. Structural analyses by room-temperature X-ray crystallography and multitemperature nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy confirm that conformational equilibria favor the target conformation. Our computational approach opens the door to targeted alterations of conformational states and equilibria, which should facilitate the design of biocatalysts with customized activity and selectivity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Sciences, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, ON, K1N 6N5, Canada.