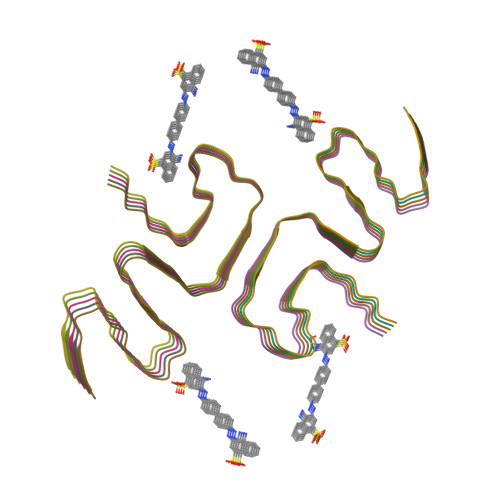
Binding adaptability of chemical ligands to polymorphic alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils.
Liu, K., Tao, Y., Zhao, Q., Xia, W., Li, X., Zhang, S., Yao, Y., Xiang, H., Han, C., Tan, L., Sun, B., Li, D., Li, A., Liu, C.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2321633121-e2321633121
- PubMed: 39172784
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2321633121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8X7L, 8X7M, 8X7O, 8X7P, 8X7Q, 8X7R, 8ZLI, 8ZLO, 8ZLP, 8ZMY - PubMed Abstract:
α-synuclein (α-syn) assembles into structurally distinct fibril polymorphs seen in different synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's disease and multiple system atrophy. Targeting these unique fibril structures using chemical ligands holds diagnostic significance for different disease subtypes. However, the molecular mechanisms governing small molecules interacting with different fibril polymorphs remain unclear. Here, we investigated the interactions of small molecules belonging to four distinct scaffolds, with different α-syn fibril polymorphs. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we determined the structures of these molecules when bound to the fibrils formed by E46K mutant α-syn and compared them to those bound with wild-type α-syn fibrils. Notably, we observed that these ligands exhibit remarkable binding adaptability, as they engage distinct binding sites across different fibril polymorphs. While the molecular scaffold primarily steered the binding locations and geometries on specific sites, the conjugated functional groups further refined this adaptable binding by fine-tuning the geometries and binding sites. Overall, our finding elucidates the adaptability of small molecules binding to different fibril structures, which sheds light on the diagnostic tracer and drug developments tailored to specific pathological fibril polymorphs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Interdisciplinary Research Center on Biology and Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201210, China.