News
2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
10/01 
The 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded jointly to James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo for their discovery of cancer therapy by inhibition of negative immune regulation.
The protein studies leading to the Nobel Prize include structures available in the PDB. James P. Allison is a coauthor on one PDB structure (T-cell immunoglobulin mucin, 2OYP) and Tasuku Honjo has contributed to two structures (PD-1/PD-L1 complex 3bik and PD-L1 3bis)
PD-1 and its ligands are a new target for cancer therapy. Our immune system walks a fine, intelligently-managed line. It needs to fight invaders, but without attacking our own cells in the process. The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) gathers information about infections and delivers it to receptors on the surface of immune system T-cells. However, the response of the immune system to this information needs to be carefully balanced, and many other molecules, such as PD-1, tune this process, stimulating and inhibiting the action of MHC and T-cell receptors as necessary.
Learn more about PD-1 (Programmed Cell Death Protein 1) at PDB-101's Molecule of the Month. Additional information is available on Tuning Immune Response with Costimulation. Browse all PDB-101 resources related to the immune system and cancer.
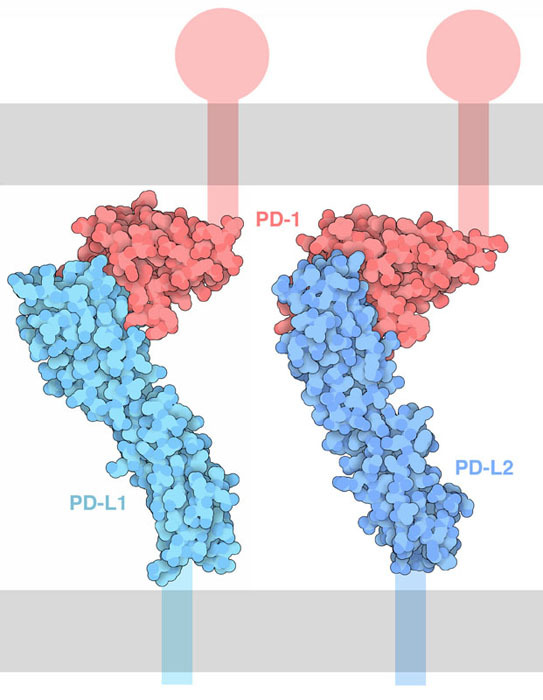 Interaction of PD-1 with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. The cell membranes are shown schematically in gray, and the portions of the proteins not included in the structure are also shown schematically. Left: Honjo's 3bik and 3bp5 from Lazar-Molnar et al.). Visit PDB-101's Molecule of the Month for more.
Interaction of PD-1 with its ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2. The cell membranes are shown schematically in gray, and the portions of the proteins not included in the structure are also shown schematically. Left: Honjo's 3bik and 3bp5 from Lazar-Molnar et al.). Visit PDB-101's Molecule of the Month for more.












